WHO European Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative: body mass index and level of overweight among 6-9-year-old children from school year 2007/2008 to school year 2009/2010
- PMID: 25099430
- PMCID: PMC4289284
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2458-14-806
WHO European Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative: body mass index and level of overweight among 6-9-year-old children from school year 2007/2008 to school year 2009/2010
Abstract
Background: The World Health Organization (WHO) Regional Office for Europe has established the Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative (COSI) to monitor changes in overweight in primary-school children. The aims of this paper are to present the anthropometric results of COSI Round 2 (2009/2010) and to explore changes in body mass index (BMI) and overweight among children within and across nine countries from school years 2007/2008 to 2009/2010.
Methods: Using cross-sectional nationally representative samples of 6-9-year-olds, BMI, anthropometric Z-scores and overweight prevalence were derived from measured weight and height. Significant changes between rounds were assessed using variance and t-tests analyses.
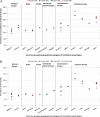
Results: At Round 2, the prevalence of overweight (including obesity; WHO definitions) ranged from 18% to 57% among boys and from 18% to 50% among girls; 6 - 31% of boys and 5 - 21% of girls were obese. Southern European countries had the highest overweight prevalence. Between rounds, the absolute change in mean BMI (range: from -0.4 to +0.3) and BMI-for-age Z-scores (range: from -0.21 to +0.14) varied statistically significantly across countries. The highest significant decrease in BMI-for-age Z-scores was found in countries with higher absolute BMI values and the highest significant increase in countries with lower BMI values. The highest significant decrease in overweight prevalence was observed in Italy, Portugal and Slovenia and the highest significant increase in Latvia and Norway.
Conclusions: Changes in BMI and prevalence of overweight over a two-year period varied significantly among European countries. It may be that countries with higher prevalence of overweight in COSI Round 1 have implemented interventions to try to remedy this situation.
Figures
References
-
- WHO Regional Office for Europe . European Charter on Counteracting Obesity. 2006.
-
- WHO Regional Office for Europe . WHO European Ministerial Conference on Counteracting Obesity. Conference report. 2007.
-
- WHO Regional Office for Europe . Vienna Declaration on Nutrition and Noncommunicable Diseases in the Context of Health 2020. 2013.
-
- WHO Regional Office for Europe . Regional Committee for Europe Resolution EUR/RC63/R4 on the Vienna Declaration on nutrition and noncommunicable diseases in the context of Health 2020. 2013.
-
- Wijnhoven TMA, van Raaij JMA, Spinelli A, Rito AI, Hovengen R, Kunesova M, Starc G, Rutter H, Sjöberg A, Petrauskiene A, O’Dwyer U, Petrova S, Farrugia Sant’Angelo V, Wauters M, Yngve A, Rubana I-M, Breda J. WHO European Childhood Obesity Surveillance Initiative 2008: weight, height and body mass index in 6–9-year-old children. Pediatr Obes. 2013;8:79–97. doi: 10.1111/j.2047-6310.2012.00090.x. - DOI - PubMed
Pre-publication history
-
- The pre-publication history for this paper can be accessed here: http://www.biomedcentral.com/1471-2458/14/806/prepub
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

