Apoptosis inducing effects of Kuding tea polyphenols in human buccal squamous cell carcinoma cell line BcaCD885
- PMID: 25100434
- PMCID: PMC4145296
- DOI: 10.3390/nu6083084
Apoptosis inducing effects of Kuding tea polyphenols in human buccal squamous cell carcinoma cell line BcaCD885
Abstract
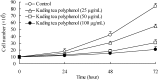
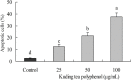
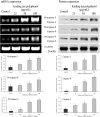
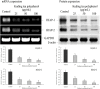
Tea polyphenols are functional substances present in tea. Kuding tea as a traditional drink also contains these compounds. After 25, 50 and 100 μg/mL of Kuding tea polyphenol treatment for 48 h, cell proliferation of human buccal squamous cell carcinoma cell line BcaCD885 was inhibited, and the 100 μg/mL of Kuding tea polyphenol showed the highest inhibitory rate at 72.3%. Compared to the lower concentration, the 100 μg/mL of Kuding tea polyphenols significantly (p < 0.05) induced apoptosis as determined by flow cytometry analysis, the content of sub-G1 cancer cells was 32.7%. By RT-PCR and western blot assays, Kuding tea polyphenol significantly induced apoptosis in BcaCD885 cancer cells (p < 0.05) by upregulating caspase-3, caspase-8, caspase-9, Fas/FasL, Bax, p53, p21, E2F1, p73 and downregulating Bcl-2, Bcl-xL, HIAP-1, and HIAP-2 mRNA and protein expressions. Kuding tea polyphenols thus present apoptosis inducing effects in vitro.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Anticancer Effect of Ursodeoxycholic Acid in Human Oral Squamous Carcinoma HSC-3 Cells through the Caspases.Nutrients. 2015 May 5;7(5):3200-18. doi: 10.3390/nu7053200. Nutrients. 2015. PMID: 25951128 Free PMC article.
-
Mdm2 inhibition induces apoptosis in p53 deficient human colon cancer cells by activating p73- and E2F1-mediated expression of PUMA and Siva-1.Apoptosis. 2011 Jan;16(1):35-44. doi: 10.1007/s10495-010-0538-0. Apoptosis. 2011. PMID: 20812030
-
In vitro and in vivo anti-cancer activities of Kuding tea (Ilex kudingcha C.J. Tseng) against oral cancer.Exp Ther Med. 2014 Mar;7(3):709-715. doi: 10.3892/etm.2013.1450. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Exp Ther Med. 2014. PMID: 24520272 Free PMC article.
-
Structure and apoptotic function of p73.BMB Rep. 2015 Feb;48(2):81-90. doi: 10.5483/bmbrep.2015.48.2.255. BMB Rep. 2015. PMID: 25441426 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical Composition, Bioactivity and Safety Aspects of Kuding Tea-From Beverage to Herbal Extract.Nutrients. 2020 Sep 12;12(9):2796. doi: 10.3390/nu12092796. Nutrients. 2020. PMID: 32932672 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anticancer Effect of Ursodeoxycholic Acid in Human Oral Squamous Carcinoma HSC-3 Cells through the Caspases.Nutrients. 2015 May 5;7(5):3200-18. doi: 10.3390/nu7053200. Nutrients. 2015. PMID: 25951128 Free PMC article.
-
Preventive Effect of Lactobacillus fermentum CQPC08 on 4-Nitroquineline-1-Oxide Induced Tongue Cancer in C57BL/6 Mice.Foods. 2019 Mar 11;8(3):93. doi: 10.3390/foods8030093. Foods. 2019. PMID: 30861992 Free PMC article.
-
Chloroplast genome structure in Ilex (Aquifoliaceae).Sci Rep. 2016 Jul 5;6:28559. doi: 10.1038/srep28559. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27378489 Free PMC article.
-
Resources and biological activities of natural polyphenols.Nutrients. 2014 Dec 22;6(12):6020-47. doi: 10.3390/nu6126020. Nutrients. 2014. PMID: 25533011 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preventive Effect of Raw Liubao Tea Polyphenols on Mouse Gastric Injuries Induced by HCl/Ethanol via Anti-Oxidative Stress.Molecules. 2018 Nov 1;23(11):2848. doi: 10.3390/molecules23112848. Molecules. 2018. PMID: 30388863 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ding B., Wang D.L., Yin J.Q., Ma W., Zhou G.Y., Long W.N. Effects of manganese on chemical qualities in Kuding tea. J. Jiangsu Forest. Sci. Technol. 2009;36:19–21.
-
- Song J.L., Qian Y., Li G.J., Zhao X. Anti-inflammatory effects of Kudingcha methanol extract (Ilex Kudingcha C.J. Tseng) in dextran sulfate sodium-induced ulcerative colitis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2013;8:1256–1262. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

