Hydrogen peroxide increases GABAA receptor-mediated tonic current in hippocampal neurons
- PMID: 25100596
- PMCID: PMC6802588
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0335-14.2014
Hydrogen peroxide increases GABAA receptor-mediated tonic current in hippocampal neurons
Abstract
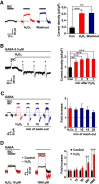
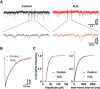
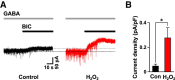
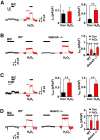
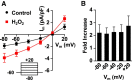
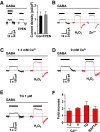
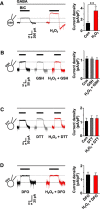
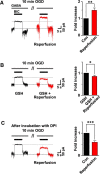
Hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), a key reactive oxygen species, is produced at low levels during normal cellular metabolism and at higher concentrations under pathological conditions such as ischemia-reperfusion injury. The mechanisms by which H2O2 contributes to physiological and pathological processes in the brain remain poorly understood. Inhibitory GABA type A (GABAA) receptors critically regulate brain function by generating tonic and synaptic currents; however, it remains unknown whether H2O2 directly modulates GABAA receptor function. Here, we performed patch-clamp recordings, together with pharmacological and genetic approaches, to investigate the effects of H2O2 on GABAA receptor-mediated tonic and synaptic currents recorded in cultured mouse hippocampal neurons and CA1 pyramidal neurons in hippocampal slices. We found that H2O2 caused a dramatic increase in tonic current, whereas synaptic currents were unaffected. This increase in tonic current resulted from an extracellular oxidative reaction, which increased the potency of GABA, but only when GABAA receptors were activated by low concentrations of GABA. Oxygen-glucose deprivation, which produces high endogenous levels of H2O2, similarly increased the tonic current. These results suggest that GABAA receptor-mediated tonic current, which is potentiated by H2O2, might contribute to H2O2-induced brain dysfunction.
Keywords: GABAA receptor; hippocampus; hydrogen peroxide; ischemia-reperfusion; mouse; tonic current.
Copyright © 2014 the authors 0270-6474/14/3410624-11$15.00/0.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
