Delineation of a FOXA1/ERα/AGR2 regulatory loop that is dysregulated in endocrine therapy-resistant breast cancer
- PMID: 25100862
- PMCID: PMC4272635
- DOI: 10.1158/1541-7786.MCR-14-0195
Delineation of a FOXA1/ERα/AGR2 regulatory loop that is dysregulated in endocrine therapy-resistant breast cancer
Abstract
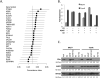
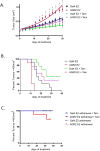
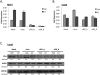
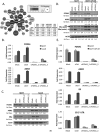
Tamoxifen, a selective estrogen receptor (ER) modulator (SERM), remains a frontline clinical therapy for patients with ERα-positive breast cancer. However, the relatively rapid development of resistance to this drug in the metastatic setting remains an impediment to a durable response. Although drug resistance likely arises by many different mechanisms, the consensus is that most of the implicated pathways facilitate the outgrowth of a subpopulation of cancer cells that can either recognize tamoxifen as an agonist or bypass the regulatory control of ERα. Notable in this regard is the observation here and in other studies that expression of anterior gradient homology 2 (AGR2), a known proto-oncogene and disulfide isomerase, was induced by both estrogen (17β-estradiol, E2) and 4-hydroxytamoxifen (4OHT) in breast cancer cells. The importance of AGR2 expression is highlighted here by the observation that (i) its knockdown inhibited the growth of both tamoxifen-sensitive and -resistant breast cancer cells and (ii) its increased expression enhanced the growth of ERα-positive tumors in vivo and increased the migratory capacity of breast cancer cells in vitro. Interestingly, as with most ERα target genes, the expression of AGR2 in all breast cancer cells examined requires the transcription factor FOXA1. However, in tamoxifen-resistant cells, the expression of AGR2 occurs in a constitutive manner, requiring FOXA1, but loses its dependence on ER. Taken together, these data define the importance of AGR2 in breast cancer cell growth and highlight a mechanism where changes in FOXA1 activity obviate the need for ER in the regulation of this gene.
Implications: These findings reveal the transcriptional interplay between FOXA1 and ERα in controlling AGR2 during the transition from therapy-sensitive to -resistant breast cancer and implicate AGR2 as a relevant therapeutic target.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures

References
-
- American Cancer Society. Facts and Figures. 2013 Available from: http://www.cancer.org/acs/groups/content/@epidemiologysurveilance/docume....
-
- Arpino G, De Angelis C, Giuliano M, Giordano A, Falato C, De Laurentiis M, et al. Molecular mechanism and clinical implications of endocrine therapy resistance in breast cancer. Oncology. 2009;77(Suppl 1):23–37. - PubMed
-
- Berstein LM, Zheng H, Yue W, Wang JP, Lykkesfeldt AE, Naftolin F, et al. New approaches to the understanding of tamoxifen action and resistance. Endocrine-related cancer. 2003;10:267–77. - PubMed
-
- Hurvitz SA, Pietras RJ. Rational management of endocrine resistance in breast cancer: a comprehensive review of estrogen receptor biology, treatment options, and future directions. Cancer. 2008;113:2385–97. - PubMed
-
- Ma XJ, Hilsenbeck SG, Wang W, Ding L, Sgroi DC, Bender RA, et al. The HOXB13:IL17BR expression index is a prognostic factor in early-stage breast cancer. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology. 2006;24:4611–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

