A deficiency of apoptosis inducing factor (AIF) in Harlequin mouse heart mitochondria paradoxically reduces ROS generation during ischemia-reperfusion
- PMID: 25101006
- PMCID: PMC4106194
- DOI: 10.3389/fphys.2014.00271
A deficiency of apoptosis inducing factor (AIF) in Harlequin mouse heart mitochondria paradoxically reduces ROS generation during ischemia-reperfusion
Abstract
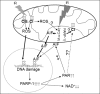
Background and aims: AIF (apoptosis inducing factor) is a flavin and NADH containing protein located within mitochondria required for optimal function of the respiratory chain. AIF may function as an antioxidant within mitochondria, yet when released from mitochondria it activates caspase-independent cell death. The Harlequin (Hq) mouse has a markedly reduced content of AIF, providing an experimental model to query if the main role of AIF in the exacerbation of cell death is enhanced mitochondrial generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) or the activation of cell death programs. We asked if the ROS generation is altered in Hq heart mitochondria at baseline or following ischemia-reperfusion (IR).
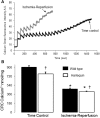
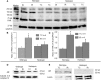
Methods: Buffer perfused mouse hearts underwent 30 min ischemia and 30 min reperfusion. Mitochondrial function including oxidative phosphorylation and H2O2 generation was measured. Immunoblotting was used to determine the contents of AIF and PAR [poly(ADP-ribose)] in cell fractions.
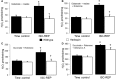
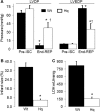
Results: There were no differences in the release of H2O2 between wild type (WT) and Hq heart mitochondria at baseline. IR increased H2O2 generation from WT but not from Hq mitochondria compared to corresponding time controls. The complex I activity was decreased in WT but not in Hq mice following IR. The relocation of AIF from mitochondria to nucleus was increased in WT but not in Hq mice. IR activated PARP-1 only in WT mice. Cell injury was decreased in the Hq mouse heart following in vitro IR.
Conclusion: A deficiency of AIF within mitochondria does not increase ROS production during IR, indicating that AIF functions less as an antioxidant within mitochondria. The decreased cardiac injury in Hq mouse heart accompanied by less AIF translocation to the nucleus suggests that AIF relocation, rather than the AIF content within mitochondria, contributes to cardiac injury during IR.
Keywords: apoptosis; electron transport chain; poly(ADP-ribose); reactive oxygen species.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardioprotection by modulation of mitochondrial respiration during ischemia-reperfusion: role of apoptosis-inducing factor.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013 Jun 14;435(4):627-33. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2013.05.033. Epub 2013 May 16. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013. PMID: 23685150
-
Astragalus membranaceus-Carthamus tinctorius herb pair antagonizes parthanatos in cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via regulating PARP-1/TAX1BP1-mediated mitochondrial respiratory chain complex I.J Ethnopharmacol. 2025 Jan 31;340:119260. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2024.119260. Epub 2024 Dec 18. J Ethnopharmacol. 2025. PMID: 39701216
-
Heart tissue of harlequin (hq)/Big Blue mice has elevated reactive oxygen species without significant impact on the frequency and nature of point mutations in nuclear DNA.Mutat Res. 2010 Sep 10;691(1-2):64-71. doi: 10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2010.06.001. Epub 2010 Jun 10. Mutat Res. 2010. PMID: 20541563
-
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 mediated caspase-independent cell death after ischemia/reperfusion.Free Radic Biol Med. 2005 Jul 1;39(1):81-90. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2005.03.021. Epub 2005 Apr 8. Free Radic Biol Med. 2005. PMID: 15925280 Review.
-
AIF, reactive oxygen species, and neurodegeneration: a "complex" problem.Neurochem Int. 2013 Apr;62(5):695-702. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2012.12.002. Epub 2012 Dec 12. Neurochem Int. 2013. PMID: 23246553 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Caspase-Dependent and Caspase-Independent Pathways Are Involved in Cadmium-Induced Apoptosis in Primary Rat Proximal Tubular Cell Culture.PLoS One. 2016 Nov 18;11(11):e0166823. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0166823. eCollection 2016. PLoS One. 2016. PMID: 27861627 Free PMC article.
-
AIF Overexpression Aggravates Oxidative Stress in Neonatal Male Mice After Hypoxia-Ischemia Injury.Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Nov;59(11):6613-6631. doi: 10.1007/s12035-022-02987-0. Epub 2022 Aug 17. Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 35974295 Free PMC article.
-
High-Resolution Respirometry for Simultaneous Measurement of Oxygen and Hydrogen Peroxide Fluxes in Permeabilized Cells, Tissue Homogenate and Isolated Mitochondria.Biomolecules. 2015 Jun 29;5(3):1319-38. doi: 10.3390/biom5031319. Biomolecules. 2015. PMID: 26131977 Free PMC article.
-
Hippocampal Neuroprotection by Minocycline and Epigallo-Catechin-3-Gallate Against Cardiopulmonary Bypass-Associated Injury.Brain Pathol. 2015 Nov;25(6):733-42. doi: 10.1111/bpa.12242. Epub 2015 Feb 15. Brain Pathol. 2015. PMID: 25582287 Free PMC article.
-
Melatonin Alleviates the Impairment of Muscle Bioenergetics and Protein Quality Control Systems in Leptin-Deficiency-Induced Obesity.Antioxidants (Basel). 2023 Nov 3;12(11):1962. doi: 10.3390/antiox12111962. Antioxidants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38001815 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

