The Trade-Off between Dietary Salt and Cardiovascular Disease; A Role for Na/K-ATPase Signaling?
- PMID: 25101054
- PMCID: PMC4101451
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2014.00097
The Trade-Off between Dietary Salt and Cardiovascular Disease; A Role for Na/K-ATPase Signaling?
Abstract
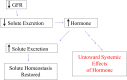
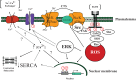
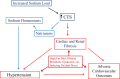
It has been postulated for some time that endogenous digitalis-like substances, also called cardiotonic steroids (CTS), exist, and that these substances are involved in sodium handling. Within the past 20 years, these substances have been unequivocally identified and measurements of circulating and tissue concentrations have been made. More recently, it has been identified that CTS also mediate signal transduction through the Na/K-ATPase, and consequently been implicated in profibrotic pathways. This review will discuss the mechanism of CTS in renal sodium handling and a potential "trade-off" effect from their role in inducing tissue fibrosis.
Keywords: cardiotonic steroids; digitalis-like factors; fibrosis; hypertension; renal failure; signaling; sodium pump.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiotonic Steroids and the Sodium Trade Balance: New Insights into Trade-Off Mechanisms Mediated by the Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 30;19(9):2576. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092576. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30200235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endogenous cardiotonic steroids and salt-sensitive hypertension.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010 Dec;1802(12):1230-6. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2010.03.011. Epub 2010 Mar 27. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2010. PMID: 20347967 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Endogenous Mammalian Cardiotonic Steroids-A New Cardiovascular Risk Factor?-A Mini-Review.Life (Basel). 2021 Jul 22;11(8):727. doi: 10.3390/life11080727. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34440471 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cardiotonic steroids in adaptation to dietary salt intake.Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2014;9(3):298-309. doi: 10.2174/1574884708666131111204031. Curr Clin Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 24219001 Review.
-
Reactive Oxygen Species Modulation of Na/K-ATPase Regulates Fibrosis and Renal Proximal Tubular Sodium Handling.Int J Nephrol. 2012;2012:381320. doi: 10.1155/2012/381320. Epub 2012 Feb 23. Int J Nephrol. 2012. PMID: 22518311 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Endogenous cardiotonic steroids in kidney failure: a review and an hypothesis.Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2015 May;22(3):232-44. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2014.12.005. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2015. PMID: 25908473 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Editorial: Natriuretic Hormones.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2015 Jul 16;6:108. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2015.00108. eCollection 2015. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2015. PMID: 26236281 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Influence of Dietary Salt Intake on T2D Treatment.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022 Jun 15;13:926143. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2022.926143. eCollection 2022. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2022. PMID: 35784580 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cardiotonic Steroids and the Sodium Trade Balance: New Insights into Trade-Off Mechanisms Mediated by the Na⁺/K⁺-ATPase.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Aug 30;19(9):2576. doi: 10.3390/ijms19092576. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30200235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The abnormalities of free fatty acid metabolism in patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, a single-center retrospective observational study.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Jun 20;24(1):312. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-03925-9. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 38902636 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Elliott P. The INTERSALT study: an addition to the evidence on salt and blood pressure, and some implications. J Hum Hypertens (1989) 3:289–98 - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

