Molecular recognition of gangliosides and their potential for cancer immunotherapies
- PMID: 25101077
- PMCID: PMC4104838
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2014.00325
Molecular recognition of gangliosides and their potential for cancer immunotherapies
Abstract
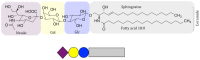
Gangliosides are sialic-acid-containing glycosphingolipids expressed on all vertebrate cells. They are primarily positioned in the plasma membrane with the ceramide part anchored in the membrane and the glycan part exposed on the surface of the cell. These lipids have highly diverse structures, not the least with respect to their carbohydrate chains, with N-acetylneuraminic acid (NeuAc) and N-glycolylneuraminic acid (NeuGc) being the two most common sialic-acid residues in mammalian cells. Generally, human healthy tissue is deficient in NeuGc, but this molecule is expressed in tumors and in human fetal tissues, and was hence classified as an onco-fetal antigen. Gangliosides perform important functions through carbohydrate-specific interactions with proteins, for example, as receptors in cell-cell recognition, which can be exploited by viruses and other pathogens, and also by regulating signaling proteins, such as the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) and the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR), through lateral interaction in the membrane. Through both mechanisms, tumor-associated gangliosides may affect malignant progression, which makes them attractive targets for cancer immunotherapies. In this review, we describe how proteins recognize gangliosides, focusing on the molecular recognition of gangliosides associated with cancer immunotherapy, and discuss the importance of these molecules in cancer research.
Keywords: biological membranes; cancer immunotherapy; cell signaling; gangliosides; glycosphingolipids; protein–carbohydrate interactions; sialic acid; tumor-associated antigens.
Figures

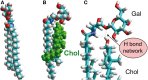
Similar articles
-
Detection of N-glycolyated gangliosides in non-small-cell lung cancer using GMR8 monoclonal antibody.Cancer Sci. 2013 Jan;104(1):43-7. doi: 10.1111/cas.12027. Epub 2012 Oct 30. Cancer Sci. 2013. PMID: 23004020 Free PMC article.
-
Gangliosides in cell recognition and membrane protein regulation.Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2009 Oct;19(5):549-57. doi: 10.1016/j.sbi.2009.06.001. Epub 2009 Jul 14. Curr Opin Struct Biol. 2009. PMID: 19608407 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of N-glycolylneuraminic acid-containing gangliosides of cat and sheep erythrocytes. 252Cf fission fragment ionization mass spectrometry in the analysis of glycosphingolipids.J Biol Chem. 1988 Oct 15;263(29):14939-47. J Biol Chem. 1988. PMID: 3170570
-
Generation of murine monoclonal antibodies specific for N-glycolylneuraminic acid-containing gangliosides.Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992 May 1;294(2):427-33. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(92)90707-4. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1992. PMID: 1567198
-
The chemical constitution of gangliosides of the vertebrate nervous system.Behav Brain Res. 1995 Jan 23;66(1-2):85-97. doi: 10.1016/0166-4328(94)00129-4. Behav Brain Res. 1995. PMID: 7755905 Review.
Cited by
-
Editorial: Structural and Computational Glycobiology - Immunity and Infection.Front Immunol. 2015 Jul 14;6:359. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00359. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 26236314 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Reprogramming the tumor microenvironment: tumor-induced immunosuppressive factors paralyze T cells.Oncoimmunology. 2015 Apr 1;4(7):e1016700. doi: 10.1080/2162402X.2015.1016700. eCollection 2015 Jul. Oncoimmunology. 2015. PMID: 26140242 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Gangliosides as Biomarkers of Human Brain Diseases: Trends in Discovery and Characterization by High-Performance Mass Spectrometry.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 8;23(2):693. doi: 10.3390/ijms23020693. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35054879 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Isobaric Labeling of Intact Gangliosides toward Multiplexed LC-MS/MS-Based Quantitative Analysis.Anal Chem. 2018 Feb 20;90(4):2578-2586. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.7b04044. Epub 2018 Jan 31. Anal Chem. 2018. PMID: 29384363 Free PMC article.
-
Routing Nanomolar Protein Cargoes to Lipid Raft-Mediated/Caveolar Endocytosis through a Ganglioside GM1-Specific Recognition Tag.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020 Jan 9;7(4):1902621. doi: 10.1002/advs.201902621. eCollection 2020 Feb. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2020. PMID: 32099761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Nomenclature Committee, Consortium for Functional Glycomics. Symbol and Text Nomenclature for Representation of Glycan Structure. (2014). Available from: http://www.functionalglycomics.org/static/consortium/Nomenclature.shtml
-
- Yu RK, Yanagisawa M, Ariga T. Glycosphingolipid structures. In: Kamerling JP, editor. Comprehensive Glycoscience (Vol. 1), Oxford: Elsevier; (2007). p. 73–122
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

