The low energy signaling network
- PMID: 25101105
- PMCID: PMC4102169
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2014.00353
The low energy signaling network
Abstract
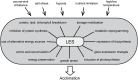
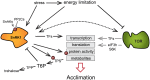
Stress impacts negatively on plant growth and crop productivity, caicultural production worldwide. Throughout their life, plants are often confronted with multiple types of stress that affect overall cellular energy status and activate energy-saving responses. The resulting low energy syndrome (LES) includes transcriptional, translational, and metabolic reprogramming and is essential for stress adaptation. The conserved kinases sucrose-non-fermenting-1-related protein kinase-1 (SnRK1) and target of rapamycin (TOR) play central roles in the regulation of LES in response to stress conditions, affecting cellular processes and leading to growth arrest and metabolic reprogramming. We review the current understanding of how TOR and SnRK1 are involved in regulating the response of plants to low energy conditions. The central role in the regulation of cellular processes, the reprogramming of metabolism, and the phenotypic consequences of these two kinases will be discussed in light of current knowledge and potential future developments.
Keywords: SnRK1; T6P; TOR; bZIP; energy signaling; metabolism; stress.
Figures


Similar articles
-
TOR and SnRK1 signaling pathways in plant response to abiotic stresses: Do they always act according to the "yin-yang" model?Plant Sci. 2019 Nov;288:110220. doi: 10.1016/j.plantsci.2019.110220. Epub 2019 Aug 16. Plant Sci. 2019. PMID: 31521220 Review.
-
HXK, SnRK1, and TOR signaling in plants: Unraveling mechanisms of stress response and secondary metabolism.Sci Prog. 2024 Oct-Dec;107(4):368504241301533. doi: 10.1177/00368504241301533. Sci Prog. 2024. PMID: 39636031 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The plant energy sensor: evolutionary conservation and divergence of SnRK1 structure, regulation, and function.J Exp Bot. 2016 Dec;67(22):6215-6252. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erw416. J Exp Bot. 2016. PMID: 27856705 Review.
-
The C/S1 bZIP Network: A Regulatory Hub Orchestrating Plant Energy Homeostasis.Trends Plant Sci. 2018 May;23(5):422-433. doi: 10.1016/j.tplants.2018.02.003. Epub 2018 Mar 7. Trends Plant Sci. 2018. PMID: 29525129 Review.
-
SnRK1 and TOR: modulating growth-defense trade-offs in plant stress responses.J Exp Bot. 2019 Apr 15;70(8):2261-2274. doi: 10.1093/jxb/erz066. J Exp Bot. 2019. PMID: 30793201 Review.
Cited by
-
Fructans Prime ROS Dynamics and Botrytis cinerea Resistance in Arabidopsis.Antioxidants (Basel). 2020 Sep 1;9(9):805. doi: 10.3390/antiox9090805. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32882794 Free PMC article.
-
Nitrogen remobilisation facilitates adventitious root formation on reversible dark-induced carbohydrate depletion in Petunia hybrida.BMC Plant Biol. 2016 Oct 10;16(1):219. doi: 10.1186/s12870-016-0901-6. BMC Plant Biol. 2016. PMID: 27724871 Free PMC article.
-
SNF1-related protein kinase 1 represses Arabidopsis growth through post-translational modification of E2Fa in response to energy stress.New Phytol. 2023 Feb;237(3):823-839. doi: 10.1111/nph.18597. Epub 2022 Dec 7. New Phytol. 2023. PMID: 36478538 Free PMC article.
-
The Juvenile Phase of Maize Sees Upregulation of Stress-Response Genes and Is Extended by Exogenous Jasmonic Acid.Plant Physiol. 2016 Aug;171(4):2648-58. doi: 10.1104/pp.15.01707. Epub 2016 Jun 15. Plant Physiol. 2016. PMID: 27307257 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptomic analysis implicates ABA signaling and carbon supply in the differential outgrowth of petunia axillary buds.BMC Plant Biol. 2023 Oct 10;23(1):482. doi: 10.1186/s12870-023-04505-3. BMC Plant Biol. 2023. PMID: 37814235 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alonso R., Oñate-Sánchez L., Weltmeier F., Ehlert A., Diaz I., Dietrich K., et al. (2009). A pivotal role of the basic leucine zipper transcription factor bZIP53 in the regulation of Arabidopsis seed maturation gene expression based on heterodimerization and protein complex formation. Plant Cell 21 1747–1761 10.1105/tpc.108.062968 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

