Preventive effects of collagen Peptide from deer sinew on bone loss in ovariectomized rats
- PMID: 25101135
- PMCID: PMC4102020
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/627285
Preventive effects of collagen Peptide from deer sinew on bone loss in ovariectomized rats
Abstract
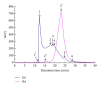
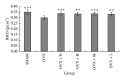
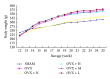
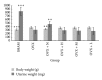
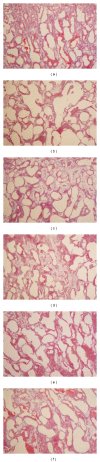
Deer sinew (DS) has been used traditionally for various illnesses, and the major active constituent is collagen. In this study, we assessed the effects of collagen peptide from DS on bone loss in the ovariectomized rats. Wister female rats were randomly divided into six groups as follows: sham-operated (SHAM), ovariectomized control (OVX), OVX given 1.0 mg/kg/week nylestriol (OVX + N), OVX given 0.4 g/kg/day collagen peptide (OVX + H), OVX given 0.2 g/kg/day collagen peptide (OXV + M), and OVX given 0.1 g/kg/day collagen peptide (OXV + L), respectively. After 13 weeks of treatment, the rats were euthanized, and the effects of collagen peptide on body weight, uterine weight, bone mineral density (BMD), serum biochemical indicators, bone histomorphometry, and bone mechanics were observed. The data showed that BMD and concentration of serum hydroxyproline were significantly increased and the levels of serum calcium, phosphorus, and alkaline phosphatase were decreased. Besides, histomorphometric parameters and mechanical indicators were improved. However, collagen peptide of DS has no effect on estradiol level, body weight, and uterine weight. Therefore, these results suggest that the collagen peptide supplementation may also prevent and treat bone loss.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Skeletal effects of parathyroid hormone infusion in ovariectomized rats with or without estrogen repletion.J Bone Miner Res. 2000 Apr;15(4):740-6. doi: 10.1359/jbmr.2000.15.4.740. J Bone Miner Res. 2000. PMID: 10780865
-
Synergistic Effects of Genistein and Zinc on Bone Metabolism and the Femoral Metaphyseal Histomorphology in the Ovariectomized Rats.Biol Trace Elem Res. 2018 Jun;183(2):288-295. doi: 10.1007/s12011-017-1134-8. Epub 2017 Aug 25. Biol Trace Elem Res. 2018. PMID: 28842860
-
Metabolomics and physiological analysis of the effect of calcium supplements on reducing bone loss in ovariectomized rats by increasing estradiol levels.Nutr Metab (Lond). 2021 Jul 23;18(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s12986-021-00602-y. Nutr Metab (Lond). 2021. PMID: 34301294 Free PMC article.
-
Antiosteoporotic activity of echinacoside in ovariectomized rats.Phytomedicine. 2013 Apr 15;20(6):549-57. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2013.01.001. Epub 2013 Feb 18. Phytomedicine. 2013. PMID: 23428402
-
A traditional Chinese herbal preparation, Er-Zhi-Wan, prevent ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2011 Nov 18;138(2):279-85. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2011.09.030. Epub 2011 Oct 5. J Ethnopharmacol. 2011. PMID: 22001072 Review.
Cited by
-
Intervention Effects of Deer-Tendon Collagen Hydrolysates on Osteoporosis In Vitro and In Vivo.Molecules. 2023 Aug 28;28(17):6275. doi: 10.3390/molecules28176275. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 37687105 Free PMC article.
-
Differentiation of deer tendons from cattle tendons by a loop-mediated isothermal amplification (LAMP) test and bone remodeling bioassays.Chin Med. 2015 Nov 12;10:33. doi: 10.1186/s13020-015-0065-6. eCollection 2015. Chin Med. 2015. PMID: 26566393 Free PMC article.
-
Protein Hydrolysates as Promoters of Non-Haem Iron Absorption.Nutrients. 2017 Jun 15;9(6):609. doi: 10.3390/nu9060609. Nutrients. 2017. PMID: 28617327 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Preparation, Characterization, and In Vitro Stability Analysis of Deer Sinew Peptide-Zinc Chelate.Foods. 2025 Jun 18;14(12):2131. doi: 10.3390/foods14122131. Foods. 2025. PMID: 40565740 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuative effects of collagen peptide from milkfish (Chanos chanos) scales on ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis.Food Sci Nutr. 2023 Oct 8;12(1):116-130. doi: 10.1002/fsn3.3746. eCollection 2024 Jan. Food Sci Nutr. 2023. PMID: 38268910 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Delmas PD. Biochemical markers of bone turnover for the clinical investigation of osteoporosis. Osteoporosis International. 1993;3(1):81–86. - PubMed
-
- McClung MR, Geusens P, Miller PD, et al. Effect of risedronate on the risk of hip fracture in elderly women. The New England Journal of Medicine. 2001;344(5):333–340. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

