The role of Nrf2-mediated pathway in cardiac remodeling and heart failure
- PMID: 25101151
- PMCID: PMC4102082
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/260429
The role of Nrf2-mediated pathway in cardiac remodeling and heart failure
Abstract
Heart failure (HF) is frequently the consequence of sustained, abnormal neurohormonal, and mechanical stress and remains a leading cause of death worldwide. The key pathophysiological process leading to HF is cardiac remodeling, a term referring to maladaptation to cardiac stress at the molecular, cellular, tissue, and organ levels. HF and many of the conditions that predispose one to HF are associated with oxidative stress. Increased generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the heart can directly lead to increased necrosis and apoptosis of cardiomyocytes which subsequently induce cardiac remodeling and dysfunction. Nuclear factor-erythroid-2- (NF-E2-) related factor 2 (Nrf2) is a transcription factor that controls the basal and inducible expression of a battery of antioxidant genes and other cytoprotective phase II detoxifying enzymes that are ubiquitously expressed in the cardiovascular system. Emerging evidence has revealed that Nrf2 and its target genes are critical regulators of cardiovascular homeostasis via the suppression of oxidative stress, which is the key player in the development and progression of HF. The purpose of this review is to summarize evidence that activation of Nrf2 enhances endogenous antioxidant defenses and counteracts oxidative stress-associated cardiac remodeling and HF.
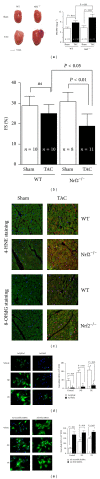
Figures

References
-
- Gutierrez J, Ballinger SW, Darley-Usmar VM, Landar A. Free radicals, mitochondria, and oxidized lipids: the emerging role in signal transduction in vascular cells. Circulation Research. 2006;99(9):924–932. - PubMed
-
- Guzik TJ, Harrison DG. Vascular NADPH oxidases as drug targets for novel antioxidant strategies. Drug Discovery Today. 2006;11(11-12):524–533. - PubMed
-
- Jialal I, Devaraj S. Antioxidants and atherosclerosis: don't throw out the baby with the bath water. Circulation. 2003;107(7):926–928. - PubMed
-
- Madamanchi NR, Vendrov A, Runge MS. Oxidative stress and vascular disease. Arteriosclerosis, Thrombosis, and Vascular Biology. 2005;25(1):29–38. - PubMed
-
- Murdoch CE, Zhang M, Cave AC, Shah AM. NADPH oxidase-dependent redox signalling in cardiac hypertrophy, remodelling and failure. Cardiovascular Research. 2006;71(2):208–215. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

