Approach to reduction of blood atherogenicity
- PMID: 25101152
- PMCID: PMC4101215
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/738679
Approach to reduction of blood atherogenicity
Abstract
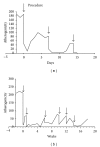
We have earlier found that blood sera of patients with coronary heart disease (CHD) increase lipid levels in cells cultured from subendothelial intima of human aorta. We have also revealed that the ability of blood sera to raise intracellular cholesterol; that is, their atherogenicity is caused by at least modified low density lipoprotein (LDL) circulating in the blood of patients and autoantibodies to modified LDL. In the present work we have demonstrated significant impact of nonlipid factor(s) to blood atherogenicity. We have developed an approach to removal of nonlipid atherogenicity factor(s) from blood serum based on the use of immobilized LDL. This approach was used for extracorporeal perfusion of patient's blood through the column with immobilized LDL. Pilot clinical study confirmed the efficacy of this approach for prevention of coronary atherosclerosis progression.
Figures

References
-
- Demarin V, Lisak M, Morović S, Cengić T. Low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol as the possible risk factor for stroke. Acta Clinica Croatica. 2010;49(4):429–439. - PubMed
-
- Libby P, Ridker PM, Hansson GK. Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature. 2011;473(7347):317–325. - PubMed
-
- Maurice P, Blaise S, Gayral S, et al. Elastin fragmentation and atherosclerosis progression: the elastokine concept. Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine. 2013;23(6):211–221. - PubMed
-
- Fogelstrand P, Borén J. Retention of atherogenic lipoproteins in the artery wall and its role in atherogenesis. Nutrition, Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases. 2012;22(1):1–7. - PubMed
-
- Chazov EI, Tertov VV, Orekhov AN, et al. Atherogenicity of blood serum from patients with coronary heart disease. The Lancet. 1986;2(8507):595–598. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

