Prevention of di (2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate-induced Testicular Disturbance in Mice by Co-administration of L-carnitine
- PMID: 25101163
- PMCID: PMC4122834
Prevention of di (2-ethylhexyl) Phthalate-induced Testicular Disturbance in Mice by Co-administration of L-carnitine
Abstract
Background: di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate (DEHP) is widely used in the plastic industry and can induce reproductive toxicity. On the other hand, L-carnitine (LC) plays a crucial role in sperm metabolism and maturation. This study evaluates the effect of LC on body and testis weight, testis tissue, count, motility, viability, morphology, and chromatin quality of epididymal sperm, testicular spermatid number (TSN) per gram testis and daily sperm production (DSP) in LC-treated mice.
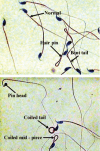
Materials and methods: IN THIS EXPERIMENTAL STUDY, ADULT MALE NMRI MICE (MEAN AGE: 4 weeks) were given doses of DEHP and LC by gavaging for 2 weeks. All samples were assessed according to World Health Organization (WHO) criteria. Sperm morphology was assessed using Papanicolaou staining and sperm chromatin quality by aniline-blue staining. The left testes were fixed in Bouinś solution for histological examination and the end slices were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E). The right testes were homogenized, and then TSN and DSP were calculated with an improved Neubauer haemocytometer and respective frames. Paired t-test, ANOVA, and Kruskal-Wallis tests were utilized for data analysis.
Results: Co-administration of DEHP and LC not only prevented significant gains in testicular weight, but also maintained the sperm's normal morphology and chromatin quality (p<0.05). In addition, LC recovered histological changes, TSN, DSP, and sperm count.
Conclusion: These results demonstrated that oral administration of LC partially or generally protects spermatogenesis from DEHP-toxicity in mice.
Keywords: L-carnitine; Spermatogenesis; Testis; di (2-ethylhexyl) phthalate.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Protective effect of alpha-lipoic acid on di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-induced testicular toxicity in mice.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Apr;27(12):13670-13678. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-07817-1. Epub 2020 Feb 7. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32030592
-
NTP technical report on the toxicity studies of Dibutyl Phthalate (CAS No. 84-74-2) Administered in Feed to F344/N Rats and B6C3F1 Mice.Toxic Rep Ser. 1995 Apr;30:1-G5. Toxic Rep Ser. 1995. PMID: 12209194
-
Beneficial role of celery oil in lowering the di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-induced testicular damage.Toxicol Ind Health. 2014 Oct;30(9):861-72. doi: 10.1177/0748233712464808. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Toxicol Ind Health. 2014. PMID: 23160384
-
Influence of di-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate on fetal testicular development by oral administration to pregnant rats.J Toxicol Sci. 2005 Aug;30(3):175-94. doi: 10.2131/jts.30.175. J Toxicol Sci. 2005. PMID: 16141652
-
Effects of L-carnitine and L-acetyl-carnitine on testicular sperm motility and chromatin quality.Iran J Reprod Med. 2012 Mar;10(2):77-82. Iran J Reprod Med. 2012. PMID: 25242977 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Protective effect of alpha-lipoic acid on di-(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate-induced testicular toxicity in mice.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020 Apr;27(12):13670-13678. doi: 10.1007/s11356-020-07817-1. Epub 2020 Feb 7. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2020. PMID: 32030592
References
-
- Akingbemi BT, Youker RT, Sottas CM, Ge R, Katz E, Klinefelter GR, et al. .Modulation of rat Leydig cell steroidogenic function by di(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate. Biol Reprod. 2001;65(4):1252–1259. - PubMed
-
- Witorsch RJ. Endocrine disruptors: can biological effects and environmental risks be predicted? Regul Toxicol Pharmacol. 2002;36(1):118–130. - PubMed
-
- Anas MK, Suzuki C, Yoshioka K, Iwamura S. Effect of mono -(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate on bovine oocyte maturation in vitro. Reprod Toxicol. 2003;17(3):305–310. - PubMed
-
- Fredricsson B, Moller L, Pousette A, Westernholm R. Human sperm motility is affected by plasticizers and diesel particle extracts. Pharmacol Toxicol. 1993;72(2):128–133. - PubMed
-
- Poon R, Lecavalier P, Mueller R, Valli VE, Procter B, Chu I. Subchronic oral toxicity of di- n- octyl phthalate and di (2- ethylhexyl) phthalate in the rat. Food Chem Toxicol. 1997;35(2):225–239. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous