Novel lutein loaded lipid nanoparticles on porcine corneal distribution
- PMID: 25101172
- PMCID: PMC4101940
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/304694
Novel lutein loaded lipid nanoparticles on porcine corneal distribution
Abstract
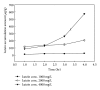
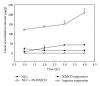
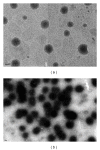
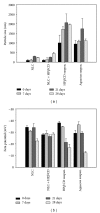
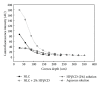
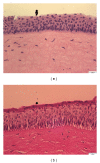
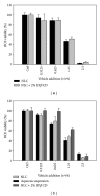
Topical delivery has the advantages including being user friendly and cost effective. Development of topical delivery carriers for lutein is becoming an important issue for the ocular drug delivery. Quantification of the partition coefficient of drug in the ocular tissue is the first step for the evaluation of delivery efficacy. The objectives of this study were to evaluate the effects of lipid nanoparticles and cyclodextrin (CD) on the corneal lutein accumulation and to measure the partition coefficients in the porcine cornea. Lipid nanoparticles combined with 2% HPβCD could enhance lutein accumulation up to 209.2 ± 18 (μg/g) which is 4.9-fold higher than that of the nanoparticles. CD combined nanoparticles have 68% of drug loading efficiency and lower cytotoxicity in the bovine cornea cells. From the confocal images, this improvement is due to the increased partitioning of lutein to the corneal epithelium by CD in the lipid nanoparticles. The novel lipid nanoparticles could not only improve the stability and entrapment efficacy of lutein but also enhance the lutein accumulation and partition in the cornea. Additionally the corneal accumulation of lutein was further enhanced by increasing the lutein payload in the vehicles.
Figures
References
-
- Kijlstra A, Tian Y, Kelly ER, Berendschot TTJM. Lutein: more than just a filter for blue light. Progress in Retinal and Eye Research. 2012;31(4):303–315. - PubMed
-
- Shoham A, Hadziahmetovic M, Dunaief JL, Mydlarski MB, Schipper HM. Oxidative stress in diseases of the human cornea. Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 2008;45(8):1047–1055. - PubMed
-
- Suh MH, Kwon J, Wee WR, Han YK, Kim JH, Lee JH. Protective effect of ascorbic acid against corneal damage by ultraviolet B irradiation: a pilot study. Cornea. 2008;27(8):916–922. - PubMed
-
- Zeng LH, Rootman DS, Fung KP, Wu TW. Comparative cytoprotection of cultured corneal endothelial cells by water- soluble antioxidants against free-radical damage. Cornea. 1995;14(5):509–514. - PubMed
-
- Jin X, Ohgami K, Shiratori K, et al. Inhibitory effects of lutein on endotoxin-induced uveitis in Lewis rats. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science. 2006;47(6):2562–2568. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

