A new mechanism for growth hormone receptor activation of JAK2, and implications for related cytokine receptors
- PMID: 25101218
- PMCID: PMC4119067
- DOI: 10.4161/jkst.29569
A new mechanism for growth hormone receptor activation of JAK2, and implications for related cytokine receptors
Abstract
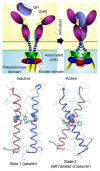
The growth hormone receptor was the first cytokine receptor to be cloned and crystallized, and provides a valuable exemplar for activation of its cognate kinase, JAK2. We review progress in understanding its activation mechanism, in particular the molecular movements made by this constitutively dimerized receptor in response to ligand binding, and how these lead to a separation of JAK-binding Box1 motifs. Such a separation leads to removal of the pseudokinase inhibitory domain from the kinase domain of a partner JAK2 bound to the receptor, and vice versa, leading to apposition of the kinase domains and transactivation. This may be a general mechanism for class I cytokine receptor action.
Keywords: Box1; FRET; conformational change; molecular dynamics; receptor dimer; transmembrane helix.
Figures
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
