Ferric chloride-induced murine carotid arterial injury: A model of redox pathology
- PMID: 25101237
- PMCID: PMC4116643
- DOI: 10.1016/j.redox.2012.11.001
Ferric chloride-induced murine carotid arterial injury: A model of redox pathology
Abstract
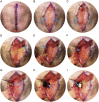
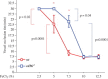
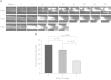
Ferric chloride (FeCl3) induced vascular injury is a widely used model of occlusive thrombosis that reports platelet activation in the context of an aseptic closed vascular system. This model is based on redox-induced endothelial cell injury, which is simple and sensitive to both anticoagulant and anti-platelets drugs. The time required for platelet aggregation to occlude blood flow gives a quantitative measure of vascular damage that is pathologically relevant to thrombotic disease. We have refined the traditional FeCl3-induced carotid artery model making the data highly reproducible with lower variation. This paper will describe our artifices and report the role of varying the oxidative damage by varying FeCl3 concentrations and exposure. To explore a maximum difference between experimental groups, adjustment of the selected FeCl3 dose and exposure duration may be necessary.
Keywords: Animal model; CA, carotid artery; Carotid artery; Ferric chloride; Thrombosis.
Figures


References
-
- Sanz J., Moreno P.R., Fuster V. The year in atherothrombosis. Journal of the American College of Cardiology. 2012;60(10):932–942. - PubMed
-
- Meadows T.A., Bhatt D.L. Clinical aspects of platelet inhibitors and thrombus formation. Circulation Research. 2007;100(9):1261–1275. May 11. - PubMed
-
- Abegunde D.O., Mathers C.D., Adam T., Ortegon M., Strong K. The burden and costs of chronic diseases in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet. 2007;370(9603):1929–1938. - PubMed
-
- Fearon I.M., Faux S.P. Oxidative stress and cardiovascular disease: novel tools give (free) radical insight. Journal of Molecular and Cellular Cardiology. 2009;47(3):372–381. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

