The role of hypoxia inducible factor-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 25101278
- PMCID: PMC4101982
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/409272
The role of hypoxia inducible factor-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
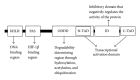
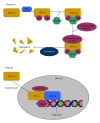
Hypoxia is a common feature of many solid tumors, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hypoxia can promote tumor progression and induce radiation and chemotherapy resistance. As one of the major mediators of hypoxic response, hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) has been shown to activate hypoxia-responsive genes, which are involved in multiple aspects of tumorigenesis and cancer progression, including proliferation, metabolism, angiogenesis, invasion, metastasis and therapy resistance. It has been demonstrated that a high level of HIF-1 in the HCC microenvironment leads to enhanced proliferation and survival of HCC cells. Accordingly, overexpression, of HIF-1 is associated with poor prognosis in HCC. In this review, we described the mechanism by which HIF-1 is regulated and how HIF-1 mediates the biological effects of hypoxia in tissues. We also summarized the latest findings concerning the role of HIF-1 in the development of HCC, which could shed light on new therapeutic approaches for the treatment of HCC.
Figures
Similar articles
-
HIF-1α promoted vasculogenic mimicry formation in hepatocellular carcinoma through LOXL2 up-regulation in hypoxic tumor microenvironment.J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017 Apr 27;36(1):60. doi: 10.1186/s13046-017-0533-1. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2017. PMID: 28449718 Free PMC article.
-
HIF-2-dependent expression of stem cell factor promotes metastasis in hepatocellular carcinoma.Cancer Lett. 2017 May 1;393:113-124. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2017.01.032. Epub 2017 Jan 30. Cancer Lett. 2017. PMID: 28153790
-
Hypoxia activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling by regulating the expression of BCL9 in human hepatocellular carcinoma.Sci Rep. 2017 Jan 11;7:40446. doi: 10.1038/srep40446. Sci Rep. 2017. PMID: 28074862 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia inducible factors in hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncotarget. 2017 Jul 11;8(28):46691-46703. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.17358. Oncotarget. 2017. PMID: 28493839 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of hypoxia in hepatocellular carcinoma metastasis.Front Med. 2014 Mar;8(1):33-41. doi: 10.1007/s11684-013-0301-3. Epub 2013 Nov 14. Front Med. 2014. PMID: 24234682 Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting carbonic anhydrase IX activity and expression.Molecules. 2015 Jan 30;20(2):2323-48. doi: 10.3390/molecules20022323. Molecules. 2015. PMID: 25647573 Free PMC article. Review.
-
SerpinB3: A Multifaceted Player in Health and Disease-Review and Future Perspectives.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Jul 18;16(14):2579. doi: 10.3390/cancers16142579. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39061218 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The role of microRNA in the resistance to treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.Ann Transl Med. 2019 Oct;7(20):577. doi: 10.21037/atm.2019.09.142. Ann Transl Med. 2019. PMID: 31807558 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Design And Characterisation Of Novel Sorafenib-Loaded Carbon Nanotubes With Distinct Tumour-Suppressive Activity In Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Int J Nanomedicine. 2019 Oct 29;14:8445-8467. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S223920. eCollection 2019. Int J Nanomedicine. 2019. PMID: 31754301 Free PMC article.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α: A critical target for inhibiting the metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma.Oncol Lett. 2022 Jun 28;24(2):284. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13404. eCollection 2022 Aug. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35814827 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Myung SJ, Yoon J. Hypoxia in hepatocellular carcinoma. The Korean journal of hepatology. 2007;13(1):9–19. - PubMed
-
- Jiang B, Rue E, Wang GL, Roe R, Semenza GL. Dimerization, DNA binding, and transactivation properties of hypoxia- inducible factor 1. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1996;271(30):17771–17778. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

