The role of hypoxia inducible factor-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma
- PMID: 25101278
- PMCID: PMC4101982
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/409272
The role of hypoxia inducible factor-1 in hepatocellular carcinoma
Abstract
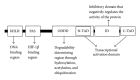
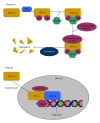
Hypoxia is a common feature of many solid tumors, including hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Hypoxia can promote tumor progression and induce radiation and chemotherapy resistance. As one of the major mediators of hypoxic response, hypoxia inducible factor-1 (HIF-1) has been shown to activate hypoxia-responsive genes, which are involved in multiple aspects of tumorigenesis and cancer progression, including proliferation, metabolism, angiogenesis, invasion, metastasis and therapy resistance. It has been demonstrated that a high level of HIF-1 in the HCC microenvironment leads to enhanced proliferation and survival of HCC cells. Accordingly, overexpression, of HIF-1 is associated with poor prognosis in HCC. In this review, we described the mechanism by which HIF-1 is regulated and how HIF-1 mediates the biological effects of hypoxia in tissues. We also summarized the latest findings concerning the role of HIF-1 in the development of HCC, which could shed light on new therapeutic approaches for the treatment of HCC.
Figures
References
-
- Myung SJ, Yoon J. Hypoxia in hepatocellular carcinoma. The Korean journal of hepatology. 2007;13(1):9–19. - PubMed
-
- Jiang B, Rue E, Wang GL, Roe R, Semenza GL. Dimerization, DNA binding, and transactivation properties of hypoxia- inducible factor 1. The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 1996;271(30):17771–17778. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

