Improvements in memory after medial septum stimulation are associated with changes in hippocampal cholinergic activity and neurogenesis
- PMID: 25101288
- PMCID: PMC4101966
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/568587
Improvements in memory after medial septum stimulation are associated with changes in hippocampal cholinergic activity and neurogenesis
Abstract
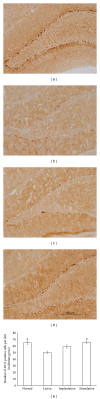
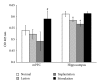
Deep brain stimulation (DBS) has been found to have therapeutic effects in patients with dementia, but DBS mechanisms remain elusive. To provide evidence for the effectiveness of DBS as a treatment for dementia, we performed DBS in a rat model of dementia with intracerebroventricular administration of 192 IgG-saporins. We utilized four groups of rats, group 1, unlesioned control; group 2, cholinergic lesion; group 3, cholinergic lesion plus medial septum (MS) electrode implantation (sham stimulation); group 4, cholinergic lesions plus MS electrode implantation and stimulation. During the probe test in the water maze, performance of the lesion group decreased for measures of time spent and the number of swim crossings over the previous platform location. Interestingly, the stimulation group showed an equivalent performance to the normal group on all measures. And these are partially reversed by the electrode implantation. Acetylcholinesterase activity in the hippocampus was decreased in lesion and implantation groups, whereas activity in the stimulation group was not different from the normal group. Hippocampal neurogenesis was increased in the stimulation group. Our results revealed that DBS of MS restores spatial memory after damage to cholinergic neurons. This effect is associated with an increase in hippocampal cholinergic activity and neurogenesis.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Identifying the appropriate time for deep brain stimulation to achieve spatial memory improvement on the Morris water maze.BMC Neurosci. 2017 Mar 7;18(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12868-017-0345-4. BMC Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28264667 Free PMC article.
-
Spatial memory alterations by activation of septal 5HT 1A receptors: no implication of cholinergic septohippocampal neurons.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011 Mar;214(2):437-54. doi: 10.1007/s00213-010-2049-7. Epub 2010 Oct 20. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2011. PMID: 20959966
-
Medial septum deep brain stimulation enhances memory and hippocampal neurogenesis in the D-galactose induced rat model of aging: behavioral and immunohistochemical study.Exp Brain Res. 2025 Mar 18;243(4):95. doi: 10.1007/s00221-025-07051-6. Exp Brain Res. 2025. PMID: 40100345
-
Immunolesion of the cholinergic basal forebrain: effects on functional properties of hippocampal and septal neurons.Int J Dev Neurosci. 1998 Nov-Dec;16(7-8):613-32. doi: 10.1016/s0736-5748(98)00073-2. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1998. PMID: 10198811 Review.
-
The Alteration of Neurogenesis and Pathological Markers in Alzheimer's Disease After Deep Brain Stimulation.Turk Neurosurg. 2022;32(4):535-548. doi: 10.5137/1019-5149.JTN.35598-21.2. Turk Neurosurg. 2022. PMID: 35147964 Review.
Cited by
-
Orientation selective DBS of entorhinal cortex and medial septal nucleus modulates activity of rat brain areas involved in memory and cognition.Sci Rep. 2022 May 20;12(1):8565. doi: 10.1038/s41598-022-12383-2. Sci Rep. 2022. PMID: 35595790 Free PMC article.
-
The medial septum controls hippocampal supra-theta oscillations.Nat Commun. 2023 Oct 10;14(1):6159. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-41746-0. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37816713 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of pregabalin on neurobehavior in an adult male rat model of PTSD.PLoS One. 2018 Dec 31;13(12):e0209494. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0209494. eCollection 2018. PLoS One. 2018. PMID: 30596711 Free PMC article.
-
Identifying the appropriate time for deep brain stimulation to achieve spatial memory improvement on the Morris water maze.BMC Neurosci. 2017 Mar 7;18(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12868-017-0345-4. BMC Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28264667 Free PMC article.
-
Compensatory remodeling of a septo-hippocampal GABAergic network in the triple transgenic Alzheimer's mouse model.J Transl Med. 2023 Apr 15;21(1):258. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04078-7. J Transl Med. 2023. PMID: 37061718 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wichmann T, DeLong MR. Deep brain stimulation for neurologic and neuropsychiatric disorders. Neuron. 2006;52(1):197–204. - PubMed
-
- Hamani C, McAndrews MP, Cohn M, et al. Memory enhancement induced by hypothalamic/fornix deep brain stimulation. Annals of Neurology. 2008;63(1):119–123. - PubMed
-
- Freund H, Kuhn J, Lenartz D, et al. Cognitive functions in a patient with parkinson-dementia syndrome undergoing deep brain stimulation. Archives of Neurology. 2009;66(6):781–785. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

