Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded RNAs: Key Molecules in Viral Pathogenesis
- PMID: 25101570
- PMCID: PMC4190559
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers6031615
Epstein-Barr Virus-Encoded RNAs: Key Molecules in Viral Pathogenesis
Abstract
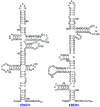
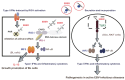
The Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is known as an oncogenic herpesvirus that has been implicated in the pathogenesis of various malignancies. EBV-encoded RNAs (EBERs) are non-coding RNAs expressed abundantly in latently EBV-infected cells. Herein, I summarize the current understanding of the functions of EBERs, including the interactions with cellular factors through which EBERs contribute to EBV-mediated pathogenesis. Previous studies have demonstrated that EBERs are responsible for malignant phenotypes in lymphoid cells, and can induce several cytokines that can promote the growth of various EBV-infected cancer cells. EBERs were also found to bind retinoic acid-inducible gene I (RIG-I) and thus activate its downstream signaling. Furthermore, EBERs induce interleukin-10, an autocrine growth factor for Burkitt's lymphoma cells, by activating RIG-I/interferon regulatory factor 3 pathway, suggesting that EBER-mediated innate immune signaling modulation contributes to EBV-mediated oncogenesis. Recently, EBV-infected cells were reported to secret EBERs, which were then recognized by toll-like receptor 3 (TLR3), leading to the induction of type I interferon and inflammatory cytokines, and subsequent immune activation. Furthermore, EBER1 was detected in the sera of patients with active EBV-infectious diseases, suggesting that EBER1-meidated TLR3 signaling activation could account for the pathogenesis of active EBV-infectious diseases.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of EBERs in the pathogenesis of EBV infection.Adv Cancer Res. 2010;107:119-36. doi: 10.1016/S0065-230X(10)07004-1. Adv Cancer Res. 2010. PMID: 20399962 Review.
-
Modulation of innate immunity system by Epstein-Barr virus-encoded non-coding RNA and oncogenesis.Cancer Sci. 2010 Jan;101(1):29-35. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.2009.01377.x. Epub 2009 Sep 29. Cancer Sci. 2010. PMID: 19886912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Multifunctional non-coding Epstein-Barr virus encoded RNAs (EBERs) contribute to viral pathogenesis.Virus Res. 2016 Jan 2;212:30-8. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2015.08.007. Epub 2015 Aug 18. Virus Res. 2016. PMID: 26292159 Review.
-
EB virus-encoded RNAs are recognized by RIG-I and activate signaling to induce type I IFN.EMBO J. 2006 Sep 20;25(18):4207-14. doi: 10.1038/sj.emboj.7601314. Epub 2006 Aug 31. EMBO J. 2006. PMID: 16946700 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr virus-encoded small RNAs (EBERs) are present in fractions related to exosomes released by EBV-transformed cells.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 4;9(6):e99163. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0099163. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24896633 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
An IL-17A-centric response to Epstein-Barr virus DNA mediated by dendritic Cell-T cell interactions.Front Mol Biosci. 2024 Apr 4;11:1243366. doi: 10.3389/fmolb.2024.1243366. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Biosci. 2024. PMID: 38638687 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus EBER Transcripts Affect miRNA-Mediated Regulation of Specific Targets and Are Processed to Small RNA Species.Noncoding RNA. 2015 Sep 30;1(3):170-191. doi: 10.3390/ncrna1030170. Noncoding RNA. 2015. PMID: 29861423 Free PMC article.
-
Herpesvirus Infection of Endothelial Cells as a Systemic Pathological Axis in Myalgic Encephalomyelitis/Chronic Fatigue Syndrome.Viruses. 2024 Apr 8;16(4):572. doi: 10.3390/v16040572. Viruses. 2024. PMID: 38675914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thermodynamic and structural characterization of an EBV infected B-cell lymphoma transcriptome.NAR Genom Bioinform. 2022 Oct 21;4(4):lqac082. doi: 10.1093/nargab/lqac082. eCollection 2022 Dec. NAR Genom Bioinform. 2022. PMID: 36285286 Free PMC article.
-
The Structure-To-Function Relationships of Gammaherpesvirus-Encoded Long Non-Coding RNAs and Their Contributions to Viral Pathogenesis.Noncoding RNA. 2018 Sep 26;4(4):24. doi: 10.3390/ncrna4040024. Noncoding RNA. 2018. PMID: 30261651 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rickinson A.B., Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus. In: Knipe D.M., Howley P.M., editors. Fields Virol. Walters Kluwer/Lippincott; Philadelphia, PA, USA: 2007. pp. 2655–2700.
-
- Chang K.L., Chen Y.Y., Shibata D., Weiss L.M. Description of an in situ hybridization methodology for detection of Epstein-Barr virus RNA in paraffin-embedded tissues, with a survey of normal and neoplastic tissues. Diagn. Mol. Pahol. 1992;1:246–255. doi: 10.1097/00019606-199203000-00037. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

