KDM6 demethylase independent loss of histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation during early embryonic development
- PMID: 25101834
- PMCID: PMC4125042
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004507
KDM6 demethylase independent loss of histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation during early embryonic development
Abstract
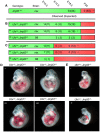
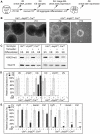
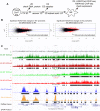
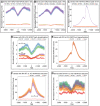
The early mammalian embryo utilizes histone H3 lysine 27 trimethylation (H3K27me3) to maintain essential developmental genes in a repressive chromatin state. As differentiation progresses, H3K27me3 is removed in a distinct fashion to activate lineage specific patterns of developmental gene expression. These rapid changes in early embryonic chromatin environment are thought to be dependent on H3K27 demethylases. We have taken a mouse genetics approach to remove activity of both H3K27 demethylases of the Kdm6 gene family, Utx (Kdm6a, X-linked gene) and Jmjd3 (Kdm6b, autosomal gene). Male embryos null for active H3K27 demethylation by the Kdm6 gene family survive to term. At mid-gestation, embryos demonstrate proper patterning and activation of Hox genes. These male embryos retain the Y-chromosome UTX homolog, UTY, which cannot demethylate H3K27me3 due to mutations in catalytic site of the Jumonji-C domain. Embryonic stem (ES) cells lacking all enzymatic KDM6 demethylation exhibit a typical decrease in global H3K27me3 levels with differentiation. Retinoic acid differentiations of these ES cells demonstrate loss of H3K27me3 and gain of H3K4me3 to Hox promoters and other transcription factors, and induce expression similar to control cells. A small subset of genes exhibit decreased expression associated with reduction of promoter H3K4me3 and some low-level accumulation of H3K27me3. Finally, Utx and Jmjd3 mutant mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) demonstrate dramatic loss of H3K27me3 from promoters of several Hox genes and transcription factors. Our results indicate that early embryonic H3K27me3 repression can be alleviated in the absence of active demethylation by the Kdm6 gene family.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


Similar articles
-
UTX and UTY demonstrate histone demethylase-independent function in mouse embryonic development.PLoS Genet. 2012 Sep;8(9):e1002964. doi: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002964. Epub 2012 Sep 27. PLoS Genet. 2012. PMID: 23028370 Free PMC article.
-
Lysine Demethylase KDM6A in Differentiation, Development, and Cancer.Mol Cell Biol. 2020 Sep 28;40(20):e00341-20. doi: 10.1128/MCB.00341-20. Print 2020 Sep 28. Mol Cell Biol. 2020. PMID: 32817139 Free PMC article. Review.
-
UTX regulates mesoderm differentiation of embryonic stem cells independent of H3K27 demethylase activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012 Sep 18;109(38):15324-9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1204166109. Epub 2012 Sep 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012. PMID: 22949634 Free PMC article.
-
Vitamin C-dependent lysine demethylase 6 (KDM6)-mediated demethylation promotes a chromatin state that supports the endothelial-to-hematopoietic transition.J Biol Chem. 2019 Sep 13;294(37):13657-13670. doi: 10.1074/jbc.RA119.009757. Epub 2019 Jul 24. J Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 31341023 Free PMC article.
-
JMJD3 as an epigenetic regulator in development and disease.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015 Oct;67:148-57. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2015.07.006. Epub 2015 Jul 17. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2015. PMID: 26193001 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Comprehensive profiling of JMJD3 in gastric cancer and its influence on patient survival.Sci Rep. 2019 Jan 29;9(1):868. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-37340-w. Sci Rep. 2019. PMID: 30696880 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-99a is a novel regulator of KDM6B-mediated osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs.J Cell Mol Med. 2018 Apr;22(4):2162-2176. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.13490. Epub 2018 Jan 29. J Cell Mol Med. 2018. PMID: 29377540 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetic Manipulation Facilitates the Generation of Skeletal Muscle Cells from Pluripotent Stem Cells.Stem Cells Int. 2017;2017:7215010. doi: 10.1155/2017/7215010. Epub 2017 Apr 9. Stem Cells Int. 2017. PMID: 28491098 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterochromatin Reduction Correlates with the Increase of the KDM4B and KDM6A Demethylases and the Expression of Pericentromeric DNA during the Acquisition of a Transformed Phenotype.J Cancer. 2017 Aug 24;8(14):2866-2875. doi: 10.7150/jca.19477. eCollection 2017. J Cancer. 2017. PMID: 28928876 Free PMC article.
-
Histone demethylases in physiology and cancer: a tale of two enzymes, JMJD3 and UTX.Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016 Feb;36:59-67. doi: 10.1016/j.gde.2016.03.010. Epub 2016 May 3. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 2016. PMID: 27151432 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Azuara V, Perry P, Sauer S, Spivakov M, Jorgensen HF, et al. (2006) Chromatin signatures of pluripotent cell lines. Nat Cell Biol 8: 532–538. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein BE, Mikkelsen TS, Xie X, Kamal M, Huebert DJ, et al. (2006) A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell 125: 315–326. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

