Hepatocyte growth factor triggers distinct mechanisms of Asef and Tiam1 activation to induce endothelial barrier enhancement
- PMID: 25101856
- PMCID: PMC4241352
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2014.07.032
Hepatocyte growth factor triggers distinct mechanisms of Asef and Tiam1 activation to induce endothelial barrier enhancement
Abstract
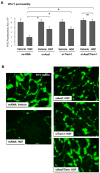
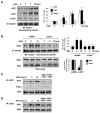
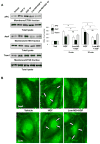
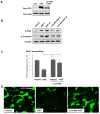
Previous reports described an important role of hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) in mitigation of pulmonary endothelial barrier dysfunction and cell injury induced by pathologic agonists and mechanical forces. HGF protective effects have been associated with Rac-GTPase signaling pathway activated by Rac-specific guanine nucleotide exchange factor Tiam1 and leading to enhancement of intercellular adherens junctions. This study tested involvement of a novel Rac-specific activator, Asef, in endothelial barrier enhancement by HGF and investigated a mechanism of HGF-induced Asef activation. Si-RNA-based knockdown of Tiam1 and Asef had an additive effect on attenuation of HGF-induced Rac activation and endothelial cell (EC) barrier enhancement. Tiam1 and Asef activation was abolished by pharmacologic inhibitors of HGF receptor and PI3-kinase. In contrast to Tiam1, Asef interacted with APC and associated with microtubule fraction upon HGF stimulation. EC treatment by low dose nocodazole to inhibit peripheral microtubule dynamics partially attenuated HGF-induced Asef peripheral translocation, but had negligible effect on Tiam1 translocation. These effects were associated with attenuation of HGF-induced barrier enhancement in EC pretreated with low ND dose and activation of Rac and its cytoskeletal effectors PAK1 and cortactin. These data demonstrate, that in addition to microtubule-independent Tiam1 activation, HGF engages additional microtubule- and APC-dependent pathway of Asef activation. These mechanisms may complement each other to provide the fine tuning of Rac signaling and endothelial barrier enhancement in response to various agonists.
Keywords: Cytoskeleton; Endothelium; Guanine nucleotide exchange factor; HGF; Permeability; Rac GTPase.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Mochizuki N. Circ J. 2009;73(12):2183–2191. - PubMed
-
- Dejana E, Tournier-Lasserve E, Weinstein BM. Dev Cell. 2009;16(2):209–221. - PubMed
-
- Beckers CM, van Hinsbergh VW, van Nieuw Amerongen GP. Thromb Haemost. 2010;103(1):40–55. - PubMed
-
- Tiruppathi C, Minshall RD, Paria BC, Vogel SM, Malik AB. Vascul Pharmacol. 2002;39(4-5):173–185. - PubMed
-
- Hirase T, Node K. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2012;302(3):H499–505. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

