A novel CDX2 isoform regulates alternative splicing
- PMID: 25101906
- PMCID: PMC4125279
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104293
A novel CDX2 isoform regulates alternative splicing
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2014;9(10):e112164. Magee, Michael [corrected to Magee, Michael S]
Abstract
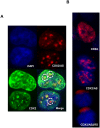
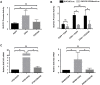
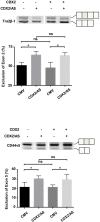
Gene expression is a dynamic and coordinated process coupling transcription with pre-mRNA processing. This regulation enables tissue-specific transcription factors to induce expression of specific transcripts that are subsequently amplified by alternative splicing allowing for increased proteome complexity and functional diversity. The intestine-specific transcription factor CDX2 regulates development and maintenance of the intestinal epithelium by inducing expression of genes characteristic of the mature enterocyte phenotype. Here, sequence analysis of CDX2 mRNA from colonic mucosa-derived tissues revealed an alternatively spliced transcript (CDX2/AS) that encodes a protein with a truncated homeodomain and a novel carboxy-terminal domain enriched in serine and arginine residues (RS domain). CDX2 and CDX2/AS exhibited distinct nuclear expression patterns with minimal areas of co-localization. CDX2/AS did not activate the CDX2-dependent promoter of guanylyl cyclase C nor inhibit transcriptional activity of CDX2. Unlike CDX2, CDX2/AS co-localized with the putative splicing factors ASF/SF2 and SC35. CDX2/AS altered splicing patterns of CD44v5 and Tra2-β1 minigenes in Lovo colon cancer cells independent of CDX2 expression. These data demonstrate unique dual functions of the CDX2 gene enabling it to regulate gene expression through both transcription (CDX2) and pre-mRNA processing (CDX2/AS).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



Similar articles
-
Extending the functions of the homeotic transcription factor Cdx2 in the digestive system through nontranscriptional activities.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Feb 7;21(5):1436-43. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i5.1436. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25663763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nuclear Speckle-related Protein 70 Binds to Serine/Arginine-rich Splicing Factors 1 and 2 via an Arginine/Serine-like Region and Counteracts Their Alternative Splicing Activity.J Biol Chem. 2016 Mar 18;291(12):6169-81. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.689414. Epub 2016 Jan 21. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 26797131 Free PMC article.
-
Cdx1 inhibits human colon cancer cell proliferation by reducing beta-catenin/T-cell factor transcriptional activity.J Biol Chem. 2004 Aug 27;279(35):36865-75. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M405213200. Epub 2004 Jun 23. J Biol Chem. 2004. PMID: 15215241
-
Caffeine regulates alternative splicing in a subset of cancer-associated genes: a role for SC35.Mol Cell Biol. 2008 Jan;28(2):883-95. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01345-07. Epub 2007 Nov 19. Mol Cell Biol. 2008. PMID: 18025108 Free PMC article.
-
Human papillomavirus regulation of SR proteins.Biochem Soc Trans. 2010 Aug;38(4):1116-21. doi: 10.1042/BST0381116. Biochem Soc Trans. 2010. PMID: 20659014 Review.
Cited by
-
Extending the functions of the homeotic transcription factor Cdx2 in the digestive system through nontranscriptional activities.World J Gastroenterol. 2015 Feb 7;21(5):1436-43. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v21.i5.1436. World J Gastroenterol. 2015. PMID: 25663763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fine-tuning and autoregulation of the intestinal determinant and tumor suppressor homeobox gene CDX2 by alternative splicing.Cell Death Differ. 2017 Dec;24(12):2173-2186. doi: 10.1038/cdd.2017.140. Epub 2017 Sep 1. Cell Death Differ. 2017. PMID: 28862703 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted CDX2 expression inhibits aggressive phenotypes of colon cancer cells in vitro and in vivo.Int J Oncol. 2017 Aug;51(2):478-488. doi: 10.3892/ijo.2017.4040. Epub 2017 Jun 13. Int J Oncol. 2017. PMID: 28627695 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bentley DL (2005) Rules of engagement: co-transcriptional recruitment of premRNA processing factors. Curr Opin Cell Biol 17: 251–256. - PubMed
-
- Das R, Yu J, Zhang Z, Gygi MP, Krainer AR, et al. (2007) SR proteins function in coupling RNAP II transcription to pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell 26: 867–881. - PubMed
-
- Phatnani HP, Greenleaf AL (2006) Phosphorylation and functions of the RNA polymerase II CTD. Genes Dev 20: 2922–2936. - PubMed
-
- Molkentin JD (2000) The zinc finger-containing transcription factors GATA-4, -5, and -6. Ubiquitously expressed regulators of tissue-specific gene expression. J Biol Chem 275: 38949–38952. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

