Structure-activity relationship of 3,5-diaryl-2-aminopyridine ALK2 inhibitors reveals unaltered binding affinity for fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva causing mutants
- PMID: 25101911
- PMCID: PMC4191596
- DOI: 10.1021/jm501177w
Structure-activity relationship of 3,5-diaryl-2-aminopyridine ALK2 inhibitors reveals unaltered binding affinity for fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva causing mutants
Abstract
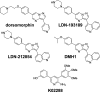
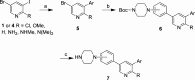
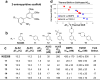
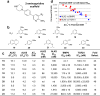
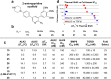
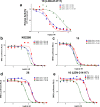
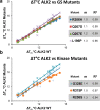
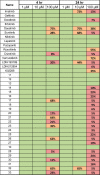
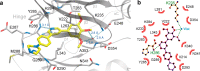
There are currently no effective therapies for fibrodysplasia ossificans progressiva (FOP), a debilitating and progressive heterotopic ossification disease caused by activating mutations of ACVR1 encoding the BMP type I receptor kinase ALK2. Recently, a subset of these same mutations of ACVR1 have been identified in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma (DIPG) tumors. Here we describe the structure-activity relationship for a series of novel ALK2 inhibitors based on the 2-aminopyridine compound K02288. Several modifications increased potency in kinase, thermal shift, or cell-based assays of BMP signaling and transcription, as well as selectivity for ALK2 versus closely related BMP and TGF-β type I receptor kinases. Compounds in this series exhibited a wide range of in vitro cytotoxicity that was not correlated with potency or selectivity, suggesting mechanisms independent of BMP or TGF-β inhibition. The study also highlights a potent 2-methylpyridine derivative 10 (LDN-214117) with a high degree of selectivity for ALK2 and low cytotoxicity that could provide a template for preclinical development. Contrary to the notion that activating mutations of ALK2 might alter inhibitor efficacy due to potential conformational changes in the ATP-binding site, the compounds demonstrated consistent binding to a panel of mutant and wild-type ALK2 proteins. Thus, BMP inhibitors identified via activity against wild-type ALK2 signaling are likely to be of clinical relevance for the diverse ALK2 mutant proteins associated with FOP and DIPG.
Figures
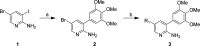
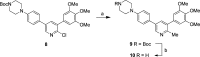

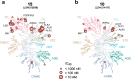
References
-
- Kitisin K.; Saha T.; Blake T.; Golestaneh N.; Deng M.; Kim C.; Tang Y.; Shetty K.; Mishra B.; Mishra L. TGF-Beta Signaling in Development. Sci. STKE 2007, 2007, cm1. - PubMed
-
- Waite K. A.; Eng C. From Developmental Disorder to Heritable Cancer: It’s All in the BMP/TGF-Beta Family. Nature Rev. Genet 2003, 4, 763–773. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y.; Massague J. Mechanisms of TGF-Beta Signaling from Cell Membrane to the Nucleus. Cell 2003, 113, 685–700. - PubMed
-
- Schmierer B.; Hill C. S. TGFbeta–SMAD Signal Transduction: Molecular Specificity and Functional Flexibility. Nature Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2007, 8, 970–982. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Chemical Information
Molecular Biology Databases

