Genome-scale co-expression network comparison across Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium reveals significant conservation at the regulon level of local regulators despite their dissimilar lifestyles
- PMID: 25101984
- PMCID: PMC4125155
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0102871
Genome-scale co-expression network comparison across Escherichia coli and Salmonella enterica serovar Typhimurium reveals significant conservation at the regulon level of local regulators despite their dissimilar lifestyles
Abstract
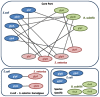
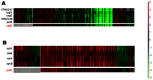
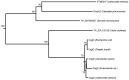
Availability of genome-wide gene expression datasets provides the opportunity to study gene expression across different organisms under a plethora of experimental conditions. In our previous work, we developed an algorithm called COMODO (COnserved MODules across Organisms) that identifies conserved expression modules between two species. In the present study, we expanded COMODO to detect the co-expression conservation across three organisms by adapting the statistics behind it. We applied COMODO to study expression conservation/divergence between Escherichia coli, Salmonella enterica, and Bacillus subtilis. We observed that some parts of the regulatory interaction networks were conserved between E. coli and S. enterica especially in the regulon of local regulators. However, such conservation was not observed between the regulatory interaction networks of B. subtilis and the two other species. We found co-expression conservation on a number of genes involved in quorum sensing, but almost no conservation for genes involved in pathogenicity across E. coli and S. enterica which could partially explain their different lifestyles. We concluded that despite their different lifestyles, no significant rewiring have occurred at the level of local regulons involved for instance, and notable conservation can be detected in signaling pathways and stress sensing in the phylogenetically close species S. enterica and E. coli. Moreover, conservation of local regulons seems to depend on the evolutionary time of divergence across species disappearing at larger distances as shown by the comparison with B. subtilis. Global regulons follow a different trend and show major rewiring even at the limited evolutionary distance that separates E. coli and S. enterica.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

