Prediabetes and lifestyle modification: time to prevent a preventable disease
- PMID: 25102521
- PMCID: PMC4116271
- DOI: 10.7812/TPP/14-002
Prediabetes and lifestyle modification: time to prevent a preventable disease
Abstract
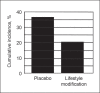
More than 100 million Americans have prediabetes or diabetes. Prediabetes is a condition in which individuals have blood glucose levels higher than normal but not high enough to be classified as diabetes. People with prediabetes have an increased risk of Type 2 diabetes. An estimated 34% of adults have prediabetes. Prediabetes is now recognized as a reversible condition that increases an individual's risk for development of diabetes. Lifestyle risk factors for prediabetes include overweight and physical inactivity.Increasing awareness and risk stratification of individuals with prediabetes may help physicians understand potential interventions that may help decrease the percentage of patients in their panels in whom diabetes develops. If untreated, 37% of the individuals with prediabetes may have diabetes in 4 years. Lifestyle intervention may decrease the percentage of prediabetic patients in whom diabetes develops to 20%.Long-term data also suggest that lifestyle intervention may decrease the risk of prediabetes progressing to diabetes for as long as 10 years. To prevent 1 case of diabetes during a 3-year period, 6.9 persons would have to participate in the lifestyle intervention program. In addition, recent data suggest that the difference in direct and indirect costs to care for a patient with prediabetes vs a patient with diabetes may be as much as $7000 per year. Investment in a diabetes prevention program now may have a substantial return on investment in the future and help prevent a preventable disease.
Figures
References
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention . National diabetes fact sheet: national estimates and general information on diabetes and prediabetes in the United States, 2011 [Internet] Atlanta, GA: US Department of Health and Human Services, Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2011. [cited 22014 Mar 3]. Available from: www.cdc.gov/diabetes/pubs/pdf/ndfs_2011_pdf.
-
- American Diabetes Association Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2011 Jan;34(Suppl 1):S62–9. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/dc11-S062. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Forouhi NG, Luan J, Hennings S, Wareham NJ. Incidence of Type 2 diabetes in England and its association with baseline impaired fasting glucose: the Ely study 1990–2000. Diabetes Med. 2007 Feb;24(2):200–7. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-5491.2007.02068.x. - DOI - PubMed
-
- American Diabetes Association Summary of revisions to the 2011 clinical practice recommendations. Diabetes Care. 2011 Jan;34(Suppl 1):S3. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/dc11-S003. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang X, Gregg EW, Williamson DF, et al. A1C level and future risk of diabetes: a systematic review. Diabetes Care. 2010 Jul;33(7):1665–73. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.2337/dc09-1939. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical