Myeloid zinc finger 1 mediates sulindac sulfide-induced upregulation of death receptor 5 of human colon cancer cells
- PMID: 25102912
- PMCID: PMC4126006
- DOI: 10.1038/srep06000
Myeloid zinc finger 1 mediates sulindac sulfide-induced upregulation of death receptor 5 of human colon cancer cells
Abstract
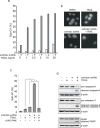
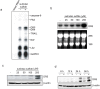
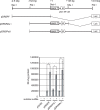
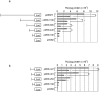
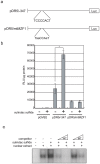
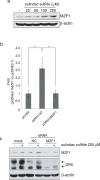
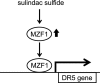
A combined therapy of sulindac sulfide and tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) is a promising strategy for the treatment of cancer. Sulindac sulfide had been shown to induce the expression of death receptor 5 (DR5), a receptor for TRAIL, and sensitize cancer cells to TRAIL-induced apoptosis; however, the molecular mechanism underlying the upregulation of DR5 has not yet been elucidated. We demonstrate here that myeloid zinc finger 1 (MZF1) mediates the induction of DR5 by sulindac sulfide. Sulindac sulfide induced the expression of DR5 at the protein and mRNA levels in colon cancer SW480 cells. Furthermore, sulindac sulfide increased DR5 promoter activity. We showed that sulindac sulfide stimulated DR5 promoter activity via the -301 to -253 region. This region contained a putative MZF1-binding site. Site-directed mutations in the site abrogated the enhancement in DR5 promoter activity by sulindac sulfide. MZF1 directly bound to the putative MZF1-binding site of the DR5 promoter and the binding was increased by sulindac sulfide. The expression of MZF1 was also increased by sulindac sulfide, and MZF1 siRNA attenuated the upregulation of DR5 by sulindac sulfide. These results indicate that sulindac sulfide induces the expression of DR5 by up-regulating MZF1.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Zinc Finger Proteins: Functions and Mechanisms in Colon Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 26;14(21):5242. doi: 10.3390/cancers14215242. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sulindac sulfide-induced apoptosis involves death receptor 5 and the caspase 8-dependent pathway in human colon and prostate cancer cells.Cancer Res. 2001 Sep 15;61(18):6918-24. Cancer Res. 2001. PMID: 11559570
-
Apo2L/TRAIL differentially modulates the apoptotic effects of sulindac and a COX-2 selective non-steroidal anti-inflammatory agent in Bax-deficient cells.Oncogene. 2002 Sep 5;21(39):6032-40. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1205897. Oncogene. 2002. PMID: 12203115
-
Sulindac sulfide-induced apoptosis is enhanced by a small-molecule Bcl-2 inhibitor and by TRAIL in human colon cancer cells overexpressing Bcl-2.Mol Cancer Ther. 2005 Oct;4(10):1475-83. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-05-0137. Mol Cancer Ther. 2005. PMID: 16227396
-
Pharmacological Small Molecules against Prostate Cancer by Enhancing Function of Death Receptor 5.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Aug 21;15(8):1029. doi: 10.3390/ph15081029. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36015177 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
MZF1 and SCAND1 Reciprocally Regulate CDC37 Gene Expression in Prostate Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Jun 8;11(6):792. doi: 10.3390/cancers11060792. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31181782 Free PMC article.
-
The Roles of Zinc Finger Proteins in Colorectal Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 16;24(12):10249. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210249. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zinc Finger Transcription Factor MZF1-A Specific Regulator of Cancer Invasion.Cells. 2020 Jan 16;9(1):223. doi: 10.3390/cells9010223. Cells. 2020. PMID: 31963147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Zinc Finger Proteins: Functions and Mechanisms in Colon Cancer.Cancers (Basel). 2022 Oct 26;14(21):5242. doi: 10.3390/cancers14215242. Cancers (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36358661 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Targeting of MZF1-AS1/PARP1/E2F1 Axis Inhibits Proline Synthesis and Neuroblastoma Progression.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019 Aug 10;6(19):1900581. doi: 10.1002/advs.201900581. eCollection 2019 Oct 2. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2019. PMID: 31592410 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Wiley S. R. et al. Identification and characterization of a new member of the TNF family that induces apoptosis. Immunity 3, 673–682 (1995). - PubMed
-
- Pitti R. M. et al. Induction of apoptosis by Apo-2 ligand, a new member of the tumor necrosis factor cytokine family. J. Biol. Chem. 271, 12687–12690 (1996). - PubMed
-
- Zerafa N. et al. Cutting edge: TRAIL deficiency accelerates hematological malignancies. J. Immunol. 175, 5586–5590 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

