Pediatric complex chronic conditions classification system version 2: updated for ICD-10 and complex medical technology dependence and transplantation
- PMID: 25102958
- PMCID: PMC4134331
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2431-14-199
Pediatric complex chronic conditions classification system version 2: updated for ICD-10 and complex medical technology dependence and transplantation
Abstract
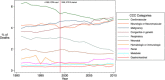
Background: The pediatric complex chronic conditions (CCC) classification system, developed in 2000, requires revision to accommodate the International Classification of Disease 10th Revision (ICD-10). To update the CCC classification system, we incorporated ICD-9 diagnostic codes that had been either omitted or incorrectly specified in the original system, and then translated between ICD-9 and ICD-10 using General Equivalence Mappings (GEMs). We further reviewed all codes in the ICD-9 and ICD-10 systems to include both diagnostic and procedural codes indicative of technology dependence or organ transplantation. We applied the provisional CCC version 2 (v2) system to death certificate information and 2 databases of health utilization, reviewed the resulting CCC classifications, and corrected any misclassifications. Finally, we evaluated performance of the CCC v2 system by assessing: 1) the stability of the system between ICD-9 and ICD-10 codes using data which included both ICD-9 codes and ICD-10 codes; 2) the year-to-year stability before and after ICD-10 implementation; and 3) the proportions of patients classified as having a CCC in both the v1 and v2 systems.
Results: The CCC v2 classification system consists of diagnostic and procedural codes that incorporate a new neonatal CCC category as well as domains of complexity arising from technology dependence or organ transplantation. CCC v2 demonstrated close comparability between ICD-9 and ICD-10 and did not detect significant discontinuity in temporal trends of death in the United States. Compared to the original system, CCC v2 resulted in a 1.0% absolute (10% relative) increase in the number of patients identified as having a CCC in national hospitalization dataset, and a 0.4% absolute (24% relative) increase in a national emergency department dataset.
Conclusions: The updated CCC v2 system is comprehensive and multidimensional, and provides a necessary update to accommodate widespread implementation of ICD-10.
Figures
References
-
- Feudtner C, Christakis DA, Connell FA. Pediatric deaths attributable to complex chronic conditions: a population-based study of Washington State, 1980-1997. Pediatrics. 2000;106:205–209. - PubMed
-
- Feudtner C, Hays RM, Haynes G, Geyer JR, Neff JM, Koepsell TD. Deaths attributed to pediatric complex chronic conditions: national trends and implications for supportive care services. Pediatrics. 2001;107:E99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical