Multidetector CT angiography influences the choice of treatment for blunt carotid artery injury
- PMID: 25103313
- PMCID: PMC4127762
- DOI: 10.1136/bcr-2013-200659
Multidetector CT angiography influences the choice of treatment for blunt carotid artery injury
Abstract
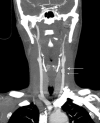
A 43-year-old woman presented with a 2 h history of left neck pain after striking her neck against a marble bench while playing with her son. The patient was screened for blunt cerebrovascular injury (BCVI) and a left carotid bruit was identified. Subsequently, she underwent multidetector CT angiography (MCTA) of the aortic arch and neck vessels, which demonstrated a flow-limiting dissection of the left common carotid artery (CCA). The patient was started on heparin infusion and underwent an emergency operation. At surgery, a circumferential intimal dissection was excised and the arteriotomy defect closed with an autologous venous patch. This case emphasises the importance of adequately examining patients with direct injury to the neck, screening relevant patients for BCVI and investigating them with MCTA that influences the choice of a treatment option.
2014 BMJ Publishing Group Ltd.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Computed tomographic angiography versus conventional angiography for the diagnosis of blunt cerebrovascular injury in trauma patients.J Trauma. 2009 Nov;67(5):1046-50. doi: 10.1097/TA.0b013e3181b83b63. J Trauma. 2009. PMID: 19901666
-
Blunt cerebrovascular injury: early recognition and treatment options in asymptomatic patient.ANZ J Surg. 2019 Apr;89(4):E166-E167. doi: 10.1111/ans.14159. Epub 2017 Oct 13. ANZ J Surg. 2019. PMID: 29027732 No abstract available.
-
Traumatic dissection of the common carotid artery after blunt injury to the neck.Surg Neurol. 1999 May;51(5):513-9; discussion 519-20. doi: 10.1016/s0090-3019(98)00102-5. Surg Neurol. 1999. PMID: 10321882
-
Multi-detector row CT angiography of the neck in blunt trauma.Radiol Clin North Am. 2012 Jan;50(1):59-72. doi: 10.1016/j.rcl.2011.08.007. Radiol Clin North Am. 2012. PMID: 22099487 Review.
-
Blunt cerebrovascular injuries: imaging with multidetector CT angiography.Radiographics. 2008 Oct;28(6):1689-708; discussion 1709-10. doi: 10.1148/rg.286085521. Radiographics. 2008. PMID: 18936030 Review.
Cited by
-
Association between cervical spine and skull-base fractures and blunt cerebrovascular injury.Eur Radiol. 2016 Feb;26(2):524-31. doi: 10.1007/s00330-015-3858-1. Epub 2015 Jun 26. Eur Radiol. 2016. PMID: 26113246
References
-
- Cook A, Osler T, Gaudet M, et al. Blunt cerebrovascular injury is poorly predicted by modeling with other injuries: analysis of NTDB data J Trauma 2011;71:114–19 - PubMed
-
- Franz R, Willette P, Wood M, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of diagnostic screening criteria for blunt cerebrovascular injuries. [Review]. J Am Coll Surg 2012;214:313–27 - PubMed
-
- Miller PR, Fabian TC, Bee TK, et al. Blunt cerebrovascular injuries: diagnosis and treatment. J Trauma 2001;51:279–85; discussion 85–6 - PubMed
-
- Burlew C, Biffl W, Moore E, et al. Blunt cerebrovascular injuries: redefining screening criteria in the era of noninvasive diagnosis. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 2012;72:330–5; discussion 6–7 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
