Validation of an automated ELISA system for detection of antibodies to Aleutian mink disease virus using blood samples collected in filter paper strips
- PMID: 25103400
- PMCID: PMC4254392
- DOI: 10.1186/1743-422X-11-141
Validation of an automated ELISA system for detection of antibodies to Aleutian mink disease virus using blood samples collected in filter paper strips
Abstract
Background: Aleutian mink disease virus (AMDV) is the cause of a chronic immune complex disease, Aleutian disease (AD), which is common in mink-producing countries. In 2005, implementation of an AMDV eradication programme in Finland created a need for an automated high-throughput assay. The aim of this study was to validate an AMDV-VP2 -recombinant antigen ELISA, which we developed earlier, in an automated assay format for the detection of anti-AMDV antibodies in mink blood and to determine the accuracy of this test compared with the reference standard (counter-current immunoelectrophoresis, CIEP).
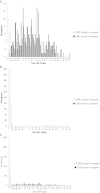
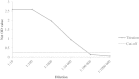
Methods: A blood sampling method based on filter paper 12-strips (blood combs) and a device to introduce these strips to an ELISA plate for elution of the samples were developed. Blood and serum samples were collected from 761 mink from two farms with low (2%) and high (81%) seroprevalences of AMDV infection in 2008. ELISA sensitivity and specificity were estimated with a Bayesian 2-test 2-population model that allowed for conditional dependence between CIEP and ELISA. Agreement between the two tests was assessed with kappa statistic and proportion agreement.
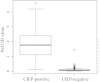
Results: The sensitivity and specificity of the automated ELISA system were estimated to be 96.2% and 98.4%, respectively. Agreement between CIEP and ELISA was high, with a kappa value of 0.976 and overall proportion agreement of 98.8%.
Conclusions: The automated ELISA system combined with blood comb sampling is an accurate test format for the detection of anti-AMDV antibodies in mink blood and offers several advantages, including improved blood sampling and data handling, fast sample throughput time, and reductions in costs and labour inputs.
Figures

Similar articles
-
AMDV Vaccine: Challenges and Perspectives.Viruses. 2021 Sep 14;13(9):1833. doi: 10.3390/v13091833. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34578415 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evaluation of two enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for serodiagnosis of Aleutian mink disease virus infection in mink.Acta Vet Scand. 2013 Nov 25;55(1):86. doi: 10.1186/1751-0147-55-86. Acta Vet Scand. 2013. PMID: 24274663 Free PMC article.
-
Development and evaluation of an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay based on recombinant VP2 capsids for the detection of antibodies to Aleutian mink disease virus.Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2009 Sep;16(9):1360-5. doi: 10.1128/CVI.00148-09. Epub 2009 Jul 29. Clin Vaccine Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19641102 Free PMC article.
-
Accuracy of enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays for quantification of antibodies against Aleutian mink disease virus.J Virol Methods. 2016 Sep;235:144-151. doi: 10.1016/j.jviromet.2016.06.004. Epub 2016 Jun 6. J Virol Methods. 2016. PMID: 27283885
-
[Research into the antibody detection technology of mink plasmacytosis and its current applications].Bing Du Xue Bao. 2015 Jan;31(1):85-90. Bing Du Xue Bao. 2015. PMID: 25997336 Review. Chinese.
Cited by
-
Serum Analytes of American Mink (Neovison Vison) Challenged with Aleutian Mink Disease Virus.Animals (Basel). 2022 Oct 11;12(20):2725. doi: 10.3390/ani12202725. Animals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290111 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of methods for detection of asymptomatic individuals infected with Leishmania infantum in the state of Piauí, Brazil.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019 Jul 1;13(7):e0007493. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0007493. eCollection 2019 Jul. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2019. PMID: 31260440 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and diagnosis of Aleutian disease caused by Aleutian mink disease virus: A literature review with a perspective of genomic breeding for disease control in American mink (Neogale vison).Virus Res. 2023 Oct 15;336:199208. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2023.199208. Epub 2023 Aug 28. Virus Res. 2023. PMID: 37633597 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dose response of black American mink to Aleutian mink disease virus.Immun Inflamm Dis. 2020 Jun;8(2):150-164. doi: 10.1002/iid3.290. Epub 2020 Mar 13. Immun Inflamm Dis. 2020. PMID: 32167659 Free PMC article.
-
AMDV Vaccine: Challenges and Perspectives.Viruses. 2021 Sep 14;13(9):1833. doi: 10.3390/v13091833. Viruses. 2021. PMID: 34578415 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- ICTV Virus Taxonomy 2013. [http://www.ictvonline.org/virusTaxonomy.asp?version=2013]
-
- Bloom ME, Kanno H, Mori S, Wolfinbarger JB. Aleutian mink disease: puzzles and paradigms. Infect Agents Dis. 1994;3:279–301. - PubMed
-
- Bossuyt PM, Reitsma JB, Bruns DE, Gatsonis CA, Glasziou PP, Irwig LM, Lijmer JG, Moher D, Rennie D, de Vet HC, Standards for Reporting of Diagnostic Accuracy Towards complete and accurate reporting of studies of diagnostic accuracy: the STARD initiative. Standards for Reporting of Diagnostic Accuracy. Clin Chem. 2003;49:1–6. doi: 10.1373/49.1.1. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

