Extensive remodeling of DC function by rapid maturation-induced transcriptional silencing
- PMID: 25104025
- PMCID: PMC4150779
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gku674
Extensive remodeling of DC function by rapid maturation-induced transcriptional silencing
Abstract
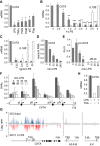
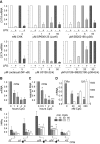
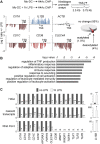
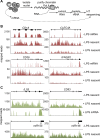
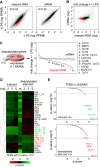
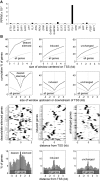
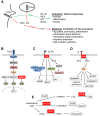
The activation, or maturation, of dendritic cells (DCs) is crucial for the initiation of adaptive T-cell mediated immune responses. Research on the molecular mechanisms implicated in DC maturation has focused primarily on inducible gene-expression events promoting the acquisition of new functions, such as cytokine production and enhanced T-cell-stimulatory capacity. In contrast, mechanisms that modulate DC function by inducing widespread gene-silencing remain poorly understood. Yet the termination of key functions is known to be critical for the function of activated DCs. Genome-wide analysis of activation-induced histone deacetylation, combined with genome-wide quantification of activation-induced silencing of nascent transcription, led us to identify a novel inducible transcriptional-repression pathway that makes major contributions to the DC-maturation process. This silencing response is a rapid primary event distinct from repression mechanisms known to operate at later stages of DC maturation. The repressed genes function in pivotal processes--including antigen-presentation, extracellular signal detection, intracellular signal transduction and lipid-mediator biosynthesis--underscoring the central contribution of the silencing mechanism to rapid reshaping of DC function. Interestingly, promoters of the repressed genes exhibit a surprisingly high frequency of PU.1-occupied sites, suggesting a novel role for this lineage-specific transcription factor in marking genes poised for inducible repression.
© The Author(s) 2014. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of Nucleic Acids Research.
Figures
References
-
- Joffre O., Nolte M.A., Sporri R., Reis e Sousa C. Inflammatory signals in dendritic cell activation and the induction of adaptive immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2009;227:234–247. - PubMed
-
- Watts C., West M.A., Zaru R. TLR signalling regulated antigen presentation in dendritic cells. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 2010;22:124–130. - PubMed
-
- Palm N.W., Medzhitov R. Pattern recognition receptors and control of adaptive immunity. Immunol. Rev. 2009;227:221–233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

