Incidence of and risk factors for sick sinus syndrome in the general population
- PMID: 25104519
- PMCID: PMC4139053
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.03.056
Incidence of and risk factors for sick sinus syndrome in the general population
Abstract
Background: Little is known about the incidence of and risk factors for sick sinus syndrome (SSS), a common indication for pacemaker implantation.
Objectives: This study sought to describe the epidemiology of SSS.
Methods: This analysis included 20,572 participants (mean baseline age 59 years, 43% male) in the ARIC (Atherosclerosis Risk In Communities) study and the CHS (Cardiovascular Health Study), who at baseline were free of prevalent atrial fibrillation and pacemaker therapy, had a heart rate of ≥ 50 beats/min unless using beta blockers, and were identified as of white or black race. Incident SSS cases were identified by hospital discharge International Classification of Disease-revision 9-Clinical Modification code 427.81 and validated by medical record review.
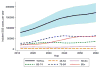
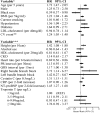
Results: During an average 17 years of follow-up, 291 incident SSS cases were identified (unadjusted rate 0.8 per 1,000 person-years). Incidence increased with age (hazard ratio [HR]: 1.73; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.47 to 2.05 per 5-year increment), and blacks had a 41% lower risk of SSS than whites (HR: 0.59; 95% CI: 0.37 to 0.98). Incident SSS was associated with greater baseline body mass index, height, N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide, and cystatin C, with longer QRS interval, with lower heart rate, and with prevalent hypertension, right bundle branch block, and cardiovascular disease. We project that the annual number of new SSS cases in the United States will increase from 78,000 in 2012 to 172,000 in 2060.
Conclusions: Blacks have a lower risk of SSS than whites, and several cardiovascular risk factors were associated with incident SSS. With the aging of the population, the number of Americans with SSS will increase dramatically over the next 50 years.
Keywords: epidemiology; pacemaker; sick sinus syndrome; tachy-brady syndrome.
Copyright © 2014 American College of Cardiology Foundation. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

Comment in
-
Sick sinus syndrome: synopsis.J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014 Aug 12;64(6):539-40. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2014.05.029. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2014. PMID: 25104520 No abstract available.
References
-
- Ferrer MI. The sick sinus syndrome. Circulation. 1973;47:635–41. - PubMed
-
- Ferrer MI. The sick sinus syndrome in atrial disease. JAMA. 1968;206:645–6. - PubMed
-
- Adan V, Crown LA. Diagnosis and treatment of sick sinus syndrome. Am Fam Physician. 2003;67:1725–32. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein AD, Parsonnet V. Survey of cardiac pacing and defibrillation in the United States in 1993. Am J Cardiol. 1996;78:187–96. - PubMed
-
- Fried LP, Borhani NO, Enright P, et al. The Cardiovascular Health Study: design and rationale. Ann Epidemiol. 1991;1:263–76. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
- N01 HC085080/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085082/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100011C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL07770/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 HL109611/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100006C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201200036C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC055222/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085081/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100012C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007902/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- T32 HL007770/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100010C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100008C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HL080295/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200800007C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085086/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085083/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100009C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268201100005C/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HC085079/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG023629/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

