General rules for the arrangements and gating motions of pore-lining helices in homomeric ion channels
- PMID: 25105557
- PMCID: PMC4133698
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms5641
General rules for the arrangements and gating motions of pore-lining helices in homomeric ion channels
Erratum in
-
Publisher Correction: General rules for the arrangements and gating motions of pore-lining helices in homomeric ion channels.Nat Commun. 2018 Apr 10;9:16210. doi: 10.1038/ncomms16210. Nat Commun. 2018. PMID: 29633764 Free PMC article.
Abstract
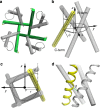
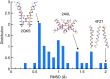
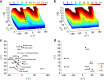
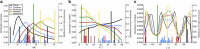
The pore-lining helix (PLH) bundles are central to the function of all ion channels, as their conformational rearrangements dictate channel gating. Here we explore all plausible oligomeric arrangements of the PLH bundles within homomeric ion channels by building models using generic restraints. In particular, the distance between two neighbouring PLHs was bounded both below and above in order to avoid steric clash and allow proper packing. The resulting models provide a theoretical representation of the accessible space for oligomeric arrangements. While the represented space is confined, it encompasses nearly all the ion channel PLH bundles for which the structures are currently known. For a multitude of channels, gating models suggested by paths within the confined accessible space are in qualitative agreement with those established in previous structural and computational studies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Proline-induced hinges in transmembrane helices: possible roles in ion channel gating.Proteins. 2001 Aug 1;44(2):63-72. doi: 10.1002/prot.1073. Proteins. 2001. PMID: 11391769
-
An energy-efficient gating mechanism in the acetylcholine receptor channel suggested by molecular and Brownian dynamics.Biophys J. 2006 Feb 1;90(3):799-810. doi: 10.1529/biophysj.105.067868. Epub 2005 Nov 11. Biophys J. 2006. PMID: 16284265 Free PMC article.
-
Geometric rules of channel gating inferred from computational models of the P2X receptor transmembrane domain.J Mol Graph Model. 2015 Sep;61:107-14. doi: 10.1016/j.jmgm.2015.06.015. Epub 2015 Jul 9. J Mol Graph Model. 2015. PMID: 26209765
-
Modelling and simulation of ion channels: applications to the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor.J Struct Biol. 1998;121(2):246-62. doi: 10.1006/jsbi.1997.3950. J Struct Biol. 1998. PMID: 9615441 Review.
-
Molecular simulation studies of hydrophobic gating in nanopores and ion channels.Biochem Soc Trans. 2015 Apr;43(2):146-50. doi: 10.1042/BST20140256. Biochem Soc Trans. 2015. PMID: 25849908 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification and Structural Characterization of Viroporins from Deadly Hemorrhagic Viruses.Viruses. 2025 Aug 14;17(8):1120. doi: 10.3390/v17081120. Viruses. 2025. PMID: 40872833 Free PMC article.
-
Toward a Model for Activation of Orai Channel.iScience. 2019 Jun 28;16:356-367. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2019.05.041. Epub 2019 Jun 1. iScience. 2019. PMID: 31207498 Free PMC article.
-
Advancing NMDA Receptor Physiology by Integrating Multiple Approaches.Trends Neurosci. 2017 Mar;40(3):129-137. doi: 10.1016/j.tins.2017.01.001. Epub 2017 Feb 8. Trends Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28187950 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rotational Dynamics of The Transmembrane Domains Play an Important Role in Peptide Dynamics of Viral Fusion and Ion Channel Forming Proteins-A Molecular Dynamics Simulation Study.Viruses. 2022 Mar 28;14(4):699. doi: 10.3390/v14040699. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 35458429 Free PMC article.
-
Dimeric Transmembrane Structure of the SARS-CoV-2 E Protein.Commun Biol. 2023 Nov 1;6(1):1109. doi: 10.1038/s42003-023-05490-x. Commun Biol. 2023. PMID: 37914906 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Miller A. N. & Long S. B. Crystal structure of the human two-pore domain potassium channel K2P1. Science 335, 432–436 (2012). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

