Structural basis of nSH2 regulation and lipid binding in PI3Kα
- PMID: 25105564
- PMCID: PMC4170646
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.2263
Structural basis of nSH2 regulation and lipid binding in PI3Kα
Abstract
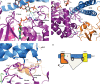
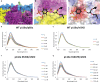
We report two crystal structures of the wild-type phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase α (PI3Kα) heterodimer refined to 2.9 Å and 3.4 Å resolution: the first as the free enzyme, the second in complex with the lipid substrate, diC4-PIP₂, respectively. The first structure shows key interactions of the N-terminal SH2 domain (nSH2) and iSH2 with the activation loop that suggest a mechanism by which the enzyme is inhibited in its basal state. In the second structure, the lipid substrate binds in a positively charged pocket adjacent to the ATP-binding site, bordered by the P-loop, the activation loop and the iSH2 domain. An additional lipid-binding site was identified at the interface of the ABD, iSH2 and kinase domains. The ability of PI3Kα to bind an additional PIP₂ molecule was confirmed in vitro by fluorescence quenching experiments. The crystal structures reveal key differences in the way the nSH2 domain interacts with wild-type p110α and with the oncogenic mutant p110αH1047R. Increased buried surface area and two unique salt-bridges observed only in the wild-type structure suggest tighter inhibition in the wild-type PI3Kα than in the oncogenic mutant. These differences may be partially responsible for the increased basal lipid kinase activity and increased membrane binding of the oncogenic mutant.
Conflict of interest statement
Under agreements between The Johns Hopkins University and various commercial entities, K.W.K. and B.V. are entitled to a share of the royalties received by The Johns Hopkins University on sales of products related to the diagnosis of mutant PIK3CA genes. The terms of these arrangements are being managed by The Johns Hopkins University in accordance with its conflict of interest policies.
Figures


References
-
- Fyffe C, Buus R, Falasca M. Genetic and Epigenetic Regulation of Phosphoinositide 3-kinase Isoforms. Curr Pharm Des. 2013;19:680–6. - PubMed
-
- Broderick DK, Di C, Parrett TJ, Samuels YR, Cummins JM, McLendon RE, Fults DW, Velculescu VE, Bigner DD, Yan H. Mutations of PIK3CA in Anaplastic Oligodendrogliomas, High-Grade Astrocytomas, and Medulloblastomas. Cancer Res. 2004;64:5048–50. - PubMed
-
- Campbell IG, Russell SE, Choong DYH, Montgomery KG, Ciavarella ML, Hooi CSF, Cristiano BE, Pearson RB, Phillips WA. Mutation of the PIK3CA gene in ovarian and breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2004;64:7678–81. - PubMed
-
- Levine DA, Bogomolniy F, Yee CJ, Lash A, Barakat RR, Borgen PI, Boyd J. Frequent mutation of the PIK3CA gene in ovarian and breast cancers. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:2875–8. - PubMed
-
- Bachman KE, Argani P, Samuels Y, Silliman N, Ptak J, Szabo S, Konishi H, Karakas B, Blair BG, Lin C, Peters BA, Velculescu VE, Park BH. The PIK3CA gene is mutated with high frequency in human breast cancers. Cancer Biol Ther. 2004;3:772–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

