Efficacy and safety of intravitreal aflibercept injection in wet age-related macular degeneration: outcomes in the Japanese subgroup of the VIEW 2 study
- PMID: 25107900
- PMCID: PMC4283691
- DOI: 10.1136/bjophthalmol-2014-305076
Efficacy and safety of intravitreal aflibercept injection in wet age-related macular degeneration: outcomes in the Japanese subgroup of the VIEW 2 study
Abstract
Background/aims: To evaluate efficacy and safety of intravitreal aflibercept (IVT-AFL) in Japanese patients with wet age-related macular degeneration (wAMD) from the VIEW 2 trial.
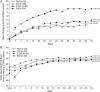
Methods: In this double-masked study, patients were randomised to: 0.5 mg IVT-AFL every 4 weeks (0.5q4); 2 mg IVT-AFL every 4 weeks (2q4); 2 mg IVT-AFL every 8 weeks (2q8) after 3 monthly injections; or 0.5 mg ranibizumab every 4 weeks (Rq4). Main efficacy outcomes included vision maintenance and best-corrected visual acuity (BCVA) at week 52.
Results: At week 52, all Japanese patients in the IVT-AFL groups (n=70) maintained vision, compared with 96% of Japanese patients (n=23/24) treated with ranibizumab. Japanese patients in all treatment groups showed improvement in BCVA after treatment. The Rq4, 2q4 and 2q8 groups experienced similar gains in BCVA from baseline. The 0.5q4 group had higher gains due to an unexpected drop in BCVA between screening and baseline. Central retinal thickness and mean area of choroidal neovascularisation decreased in all treatment groups with similar magnitude. Ocular treatment-emergent adverse events were balanced across treatment groups.
Conclusions: IVT-AFL was effective and well tolerated in Japanese patients. Outcomes in this population were consistent with those in the overall VIEW 2 population.
Trial registration number: NCT00637377.
Keywords: Angiogenesis; Clinical Trial; Macula; Neovascularisation; Retina.
Published by the BMJ Publishing Group Limited. For permission to use (where not already granted under a licence) please go to http://group.bmj.com/group/rights-licensing/permissions.
Figures
References
-
- Heier JS, Brown DM, Chong V, et al. Intravitreal aflibercept (VEGF trap-eye) in wet age-related macular degeneration. Ophthalmology 2012;119:2537–48. - PubMed
-
- Bird AC. The Bowman lecture. Towards an understanding of age-related macular disease. Eye (Lond) 2003;17:457–66. - PubMed
-
- Kawasaki R, Wang JJ, Ji GJ, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for age-related macular degeneration in an adult Japanese population: the Funagata study. Ophthalmology 2008;115:1376–81, 1381. - PubMed
-
- Maruko I, Iida T, Saito M, et al. Clinical characteristics of exudative age-related macular degeneration in Japanese patients. Am J Ophthalmol 2007;144:15–22. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical