Phase II study of cetuximab in combination with cisplatin and radiation in unresectable, locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Eastern cooperative oncology group trial E3303
- PMID: 25107914
- PMCID: PMC4184913
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-14-0051
Phase II study of cetuximab in combination with cisplatin and radiation in unresectable, locally advanced head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: Eastern cooperative oncology group trial E3303
Abstract
Purpose: Treatment with cisplatin or cetuximab combined with radiotherapy each yield superior survival in locally advanced squamous cell head and neck cancer (LA-SCCHN) compared with radiotherapy alone. Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Trial E3303 evaluated the triple combination.
Experimental design: Patients with stage IV unresectable LA-SCCHN received a loading dose of cetuximab (400 mg/m(2)) followed by 250 mg/m(2)/week and cisplatin 75 mg/m(2) q 3 weeks ×3 cycles concurrent with standard fractionated radiotherapy. In the absence of disease progression or unacceptable toxicity, patients continued maintenance cetuximab for 6 to 12 months. Primary endpoint was 2-year progression-free survival (PFS). Patient tumor and blood correlates, including tumor human papillomavirus (HPV) status, were evaluated for association with survival.
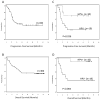
Results: A total of 69 patients were enrolled; 60 proved eligible and received protocol treatment. Oropharyngeal primaries constituted the majority (66.7%), stage T4 48.3% and N2-3 91.7%. Median radiotherapy dose delivered was 70 Gy, 71.6% received all three cycles of cisplatin, and 74.6% received maintenance cetuximab. Median PFS was 19.4 months, 2-year PFS 47% [95% confidence interval (CI), 33%-61%]. Two-year overall survival (OS) was 66% (95% CI, 53%-77%); median OS was not reached. Response rate was 66.7%. Most common grade ≥3 toxicities included mucositis (55%), dysphagia (46%), and neutropenia (26%); one attributable grade 5 toxicity occurred. Only tumor HPV status was significantly associated with survival. HPV was evaluable in 29 tumors; 10 (all oropharyngeal) were HPV positive. HPV(+) patients had significantly longer OS and PFS (P = 0.004 and P = 0.036, respectively).
Conclusions: Concurrent cetuximab, cisplatin, and radiotherapy were well tolerated and yielded promising 2-year PFS and OS in LA-SCCHN with improved survival for patients with HPV(+) tumors.
©2014 American Association for Cancer Research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have the following potential conflicts of interest to declare:
Figures

References
-
- Vokes E, Weichselbaum RR, Lippman SM, Hong WK. Head and neck cancer. NEJM. 1993;328:184–94. - PubMed
-
- Adelstein DJ, Tan EH, Lavertu P. Treatment of head and neck cancer: the role of chemotherapy. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 1996;24:97–116. - PubMed
-
- Haddad RI, Shin DM. Recent advances in head and neck cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1143–54. - PubMed
-
- Adelstein DJ, Li Y, Adams GL, Wagner H, Jr, Kish JA, Ensley JF, et al. An intergroup phase III comparison of standard radiation therapy and two schedules of concurrent chemoradiotherapy in patients with unresectable squamous cell head and neck cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2003;21:92–8. - PubMed
-
- Adelstein DJ, Saxton JP, Lavertu P, Tuason L, Wood BG, Wanamaker JR, et al. A phase III randomized trial comparing concurrent chemotherapy and radiotherapy with radiotherapy alone in resectable stage III and IV squamous cell head and neck cancer: preliminary results. Head Neck. 1997;19:567–75. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA137140/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA66636/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA021115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA27525/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA066636/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA016116/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA16116/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA027525/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- K07 CA137140/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA039229/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA39229/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180820/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA023318/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA180794/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA15488/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA21115/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U24 CA114737/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA23318/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U10 CA015488/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE023685/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

