Effect of statins on endothelial function in patients with acute coronary syndrome: a prospective study using adhesion molecules and flow-mediated dilatation
- PMID: 25110539
- PMCID: PMC4125330
- DOI: 10.14740/jocmr1863w
Effect of statins on endothelial function in patients with acute coronary syndrome: a prospective study using adhesion molecules and flow-mediated dilatation
Abstract
Background: Accumulating evidence suggests that inflammatory mechanisms play a central role in the development, progression and outcome of atherosclerosis. Recent evidence suggests that statins improve anti-inflammatory, anti-thrombotic and endothelial functions, along with their lipid-decreasing effects. We examined the effect of statins on endothelial function using biochemical markers of endothelial dysfunction and brachial artery flow-mediated dilatation (FMD).
Methods: Thirty male patients presenting with acute coronary syndrome (ACS) and 26 age-matched healthy control subjects aged 40 - 60 years who were not on any medication were enrolled in the study. The patient group was started on atorvastatin (40 mg/day) without consideration of their low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholesterol levels. Endothelin, sICAM and E-selectin from stored serum samples were measured using commercially available enzyme-linked immunosorbant assays (ELISAs). Endothelial function was assessed using brachial artery FMD.
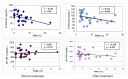
Results: Prior to statin treatment, E-selectin, sICAM and endothelin levels, endothelial dysfunction markers, were 99.74 ± 34.67 ng/mL, 568.8 ± 149.0 ng/mL and 0.62 ± 0.33 fmol/mL, respectively in the patient group. E-selectin and sICAM levels were significantly higher in the patients than in the control subjects (P < 0.001); however, endothelin levels were not significantly different between groups. Statin treatment significantly reduced E-selectin and sICAM levels (P < 0.001); however, the decrease in endothelin levels was not statistically significant. %FMD values were significantly increased after statin treatment (P = 0.005), and levels of C-reactive protein (CRP), an inflammation marker, were significantly reduced.
Conclusion: Our results indicate that statins play an important role in treatment endothelial dysfunction by reducing adhesion of inflammatory cells.
Keywords: Acute coronary syndrome; Adhesion molecules; Flow-mediated dilatation; Statins; Ultrasonography.
Figures
References
-
- Di Corleto PE, Gimbrone MA. In: Atherosclerosis and Coronary Artery Disease, Vol. 1. Fuster V, Ross R, Topol EJ, editors. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven; 1996. Vascular Endothelium.
-
- Tunstall-Pedoe H, Kuulasmaa K, Amouyel P, Arveiler D, Rajakangas AM, Pajak A. Myocardial infarction and coronary deaths in the World Health Organization MONICA Project. Myocardial infarction and coronary deaths in the World Health Organization MONICA Project. Circulation. 1994;90(1):583–612. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.90.1.583. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous