Combating unmeasured confounding in cross-sectional studies: evaluating instrumental-variable and Heckman selection models
- PMID: 25110904
- PMCID: PMC4217491
- DOI: 10.1037/a0037416
Combating unmeasured confounding in cross-sectional studies: evaluating instrumental-variable and Heckman selection models
Abstract
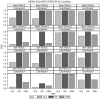
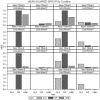
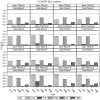
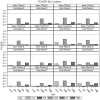
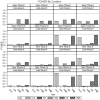
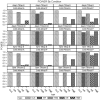
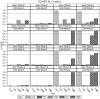
Unmeasured confounding is the principal threat to unbiased estimation of treatment "effects" (i.e., regression parameters for binary regressors) in nonexperimental research. It refers to unmeasured characteristics of individuals that lead them both to be in a particular "treatment" category and to register higher or lower values than others on a response variable. In this article, I introduce readers to 2 econometric techniques designed to control the problem, with a particular emphasis on the Heckman selection model (HSM). Both techniques can be used with only cross-sectional data. Using a Monte Carlo experiment, I compare the performance of instrumental-variable regression (IVR) and HSM to that of ordinary least squares (OLS) under conditions with treatment and unmeasured confounding both present and absent. I find HSM generally to outperform IVR with respect to mean-square-error of treatment estimates, as well as power for detecting either a treatment effect or unobserved confounding. However, both HSM and IVR require a large sample to be fully effective. The use of HSM and IVR in tandem with OLS to untangle unobserved confounding bias in cross-sectional data is further demonstrated with an empirical application. Using data from the 2006-2010 General Social Survey (National Opinion Research Center, 2014), I examine the association between being married and subjective well-being.
PsycINFO Database Record (c) 2014 APA, all rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
The impact of unmeasured within- and between-cluster confounding on the bias of effect estimatorsof a continuous exposure.Stat Methods Med Res. 2020 Aug;29(8):2119-2139. doi: 10.1177/0962280219883323. Epub 2019 Nov 7. Stat Methods Med Res. 2020. PMID: 31694489
-
Assessing causal treatment effect estimation when using large observational datasets.BMC Med Res Methodol. 2019 Nov 14;19(1):207. doi: 10.1186/s12874-019-0858-x. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2019. PMID: 31726969 Free PMC article.
-
Sample size importantly limits the usefulness of instrumental variable methods, depending on instrument strength and level of confounding.J Clin Epidemiol. 2014 Nov;67(11):1258-64. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2014.05.019. Epub 2014 Aug 12. J Clin Epidemiol. 2014. PMID: 25124167
-
Adjusting for unmeasured confounding in nonrandomized longitudinal studies: a methodological review.J Clin Epidemiol. 2017 Jul;87:23-34. doi: 10.1016/j.jclinepi.2017.04.022. Epub 2017 Apr 28. J Clin Epidemiol. 2017. PMID: 28460857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Methods to control for unmeasured confounding in pharmacoepidemiology: an overview.Int J Clin Pharm. 2016 Jun;38(3):714-23. doi: 10.1007/s11096-016-0299-0. Epub 2016 Apr 18. Int J Clin Pharm. 2016. PMID: 27091131 Review.
Cited by
-
Associations between older African academics' physical activity, walkability and mental health: a social distancing perspective.Health Promot Int. 2022 Apr 29;37(2):daab093. doi: 10.1093/heapro/daab093. Health Promot Int. 2022. PMID: 34543431 Free PMC article.
-
Associations Between Shift Work, Sociodemographic and Lifestyle Characteristics, Body Measurements, and MASLD.Life (Basel). 2025 Jun 16;15(6):961. doi: 10.3390/life15060961. Life (Basel). 2025. PMID: 40566613 Free PMC article.
-
The Cortisol Assessment List (CoAL) A tool to systematically document and evaluate cortisol assessment in blood, urine and saliva.Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2021 Dec 28;9:100108. doi: 10.1016/j.cpnec.2021.100108. eCollection 2022 Feb. Compr Psychoneuroendocrinol. 2021. PMID: 35755928 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Availability and Affordability of Primary Health Care Among Vulnerable Populations in Urban Kumasi Metropolis: Family Health Perspective.Health Equity. 2022 May 11;6(1):345-355. doi: 10.1089/heq.2021.0045. eCollection 2022. Health Equity. 2022. PMID: 35651354 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Integrating Machine Learning in Comparative Effectiveness Research of Oral Anticoagulants in Patients with Atrial Fibrillation.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 Oct 9;19(19):12916. doi: 10.3390/ijerph191912916. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 36232216 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Allison PD. Missing data. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage; 2002.
-
- Allison PD. Fixed effects regression methods for longitudinal data using SAS. Cary, NC: SAS Institute; 2005.
-
- Allison PD. Fixed effects regression models. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage; 2009.
-
- Angrist JD. Lifetime earnings and the Vietnam era draft lottery: Evidence from Social Security administrative records. American Economic Review. 1990;80:313–335.
-
- Angrist JD. National Bureau of Economic Research Technical Working Paper No 115. Cambridge, MA: National Bureau of Economic Research; 1991. Instrumental variables estimation of average treatment effects in econometrics and epidemiology.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

