Optical Coherence Tomography angiography reveals laminar microvascular hemodynamics in the rat somatosensory cortex during activation
- PMID: 25111471
- PMCID: PMC4253684
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.08.004
Optical Coherence Tomography angiography reveals laminar microvascular hemodynamics in the rat somatosensory cortex during activation
Abstract
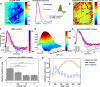
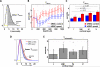
The BOLD (blood-oxygen-level dependent) fMRI (functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging) signal is shaped, in part, by changes in red blood cell (RBC) content and flow across vascular compartments over time. These complex dynamics have been challenging to characterize directly due to a lack of appropriate imaging modalities. In this study, making use of infrared light scattering from RBCs, depth-resolved Optical Coherence Tomography (OCT) angiography was applied to image laminar functional hyperemia in the rat somatosensory cortex. After defining and validating depth-specific metrics for changes in RBC content and speed, laminar hemodynamic responses in microvasculature up to cortical depths of >1mm were measured during a forepaw stimulus. The results provide a comprehensive picture of when and where changes in RBC content and speed occur during and immediately following cortical activation. In summary, the earliest and largest microvascular RBC content changes occurred in the middle cortical layers, while post-stimulus undershoots were most prominent superficially. These laminar variations in positive and negative responses paralleled known distributions of excitatory and inhibitory synapses, suggesting neuronal underpinnings. Additionally, the RBC speed response consistently returned to baseline more promptly than RBC content after the stimulus across cortical layers, supporting a "flow-volume mismatch" of hemodynamic origin.
Keywords: Blood volume; Blood-oxygen-level-dependent; Forepaw; Hematocrit; Hemodynamics; Laminar; Neurovascular coupling; Optical Coherence Tomography; Scattering; Somatosensory cortex; Three-dimensional microscopy; functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


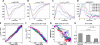



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

