A contact-imaging based microfluidic cytometer with machine-learning for single-frame super-resolution processing
- PMID: 25111497
- PMCID: PMC4128713
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0104539
A contact-imaging based microfluidic cytometer with machine-learning for single-frame super-resolution processing
Abstract
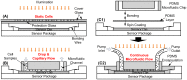
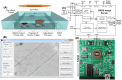
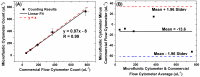
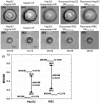
Lensless microfluidic imaging with super-resolution processing has become a promising solution to miniaturize the conventional flow cytometer for point-of-care applications. The previous multi-frame super-resolution processing system can improve resolution but has limited cell flow rate and hence low throughput when capturing multiple subpixel-shifted cell images. This paper introduces a single-frame super-resolution processing with on-line machine-learning for contact images of cells. A corresponding contact-imaging based microfluidic cytometer prototype is demonstrated for cell recognition and counting. Compared with commercial flow cytometer, less than 8% error is observed for absolute number of microbeads; and 0.10 coefficient of variation is observed for cell-ratio of mixed RBC and HepG2 cells in solution.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




References
-
- Shapiro HM (2003) Practical Flow Cytometry, 4th Edition, Wiley.
-
- Givan A (2001) Flow cytometry: first principles, John Wiley & Sons.
-
- Brown M, Wittwer C (2000) Flow cytometry: principles and clinical applications in hematology. Clinical Chemistry 46: 1221–1229. - PubMed
-
- Gupta GP, Massagué J (2006) Cancer metastasis: building a framework. Cell 127: 679–695. - PubMed
-
- Hammer SM, Eron JJ, Reiss P (2008) Schooley RT, Thompson MA, et al (2008) Antiretroviral treatment of adult HIV infection. Journal of the American Medical Association 300: 555–570. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

