Protein-engineered hydrogel encapsulation for 3-D culture of murine cochlea
- PMID: 25111520
- PMCID: PMC4905747
- DOI: 10.1097/MAO.0000000000000518
Protein-engineered hydrogel encapsulation for 3-D culture of murine cochlea
Abstract
Hypothesis: Elastin-like protein (ELP) hydrogel helps maintain the three-dimensional (3-D) cochlear structure in culture.
Background: Whole-organ culture of the cochlea is a useful model system facilitating manipulation and analysis of live sensory cells and surrounding nonsensory cells. The precisely organized 3-D cochlear structure demands a culture method that preserves this delicate architecture; however, current methods have not been optimized to serve such a purpose.
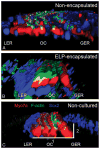
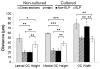
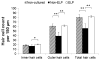
Methods: A protein-engineered ELP hydrogel was used to encapsulate organ of Corti isolated from neonatal mice. Cultured cochleae were immunostained for markers of hair cells and supporting cells. Organ of Corti hair cell and supporting cell density and organ dimensions were compared between the ELP and nonencapsulated systems. These culture systems were then compared with noncultured cochlea.
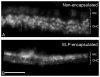
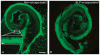
Results: After 3 days in vitro, vital dye uptake and immunostaining for sensory and nonsensory cells show that encapsulated cochlea contain viable cells with an organized architecture. In comparison with nonencapsulated cultured cochlea, ELP-encapsulated cochleae exhibit higher densities of hair cells and supporting cells and taller and narrower organ of Corti dimensions that more closely resemble those of noncultured cochleae. However, we found compromised cell viability when the culture period extended beyond 3 days.
Conclusion: We conclude that the ELP hydrogel can help preserve the 3-D architecture of neonatal cochlea in short-term culture, which may be applicable to in vitro study of the physiology and pathophysiology of the inner ear.
Figures


Similar articles
-
BMP signaling is necessary for patterning the sensory and nonsensory regions of the developing mammalian cochlea.J Neurosci. 2010 Nov 10;30(45):15044-51. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3547-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 21068310 Free PMC article.
-
Peptide- and collagen-based hydrogel substrates for in vitro culture of chick cochleae.Biomaterials. 2008 Mar;29(8):1028-42. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2007.11.006. Epub 2007 Nov 26. Biomaterials. 2008. PMID: 18037163 Free PMC article.
-
An in vitro preparation to access cellular and neuronal components in the mouse inner ear.J Neurocytol. 2000 Sep;29(9):645-52. doi: 10.1023/a:1010831303845. J Neurocytol. 2000. PMID: 11353288
-
Strategies for replacing lost cochlear hair cells.Neuroreport. 2004 May 19;15(7):1089-92. doi: 10.1097/00001756-200405190-00001. Neuroreport. 2004. PMID: 15129151 Review.
-
Postnatal development, maturation and aging in the mouse cochlea and their effects on hair cell regeneration.Hear Res. 2013 Mar;297:68-83. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2012.11.009. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Hear Res. 2013. PMID: 23164734 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Enhancing Peptide Biomaterials for Biofabrication.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Aug 4;13(16):2590. doi: 10.3390/polym13162590. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34451130 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protein-Engineered Functional Materials.Adv Healthc Mater. 2019 Jun;8(11):e1801374. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201801374. Epub 2019 Apr 2. Adv Healthc Mater. 2019. PMID: 30938924 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Optimizing Factors in Murine Whole-Organ Cochlea Culture.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 Apr 21;26(8):3908. doi: 10.3390/ijms26083908. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40332783 Free PMC article.
-
Approaches for the study of epigenetic modifications in the inner ear and related tissues.Hear Res. 2019 May;376:69-85. doi: 10.1016/j.heares.2019.01.007. Epub 2019 Jan 12. Hear Res. 2019. PMID: 30679030 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro culture of mammalian inner ear hair cells.J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2019 Feb.;20(2):170-179. doi: 10.1631/jzus.B1700613. Epub 2018 Sep 6. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 2019. PMID: 30187712 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ding D, Allman BL, Salvi R. Review: ototoxic characteristics of platinum antitumor drugs. Anat Rec. 2012;295:1851–67. - PubMed
-
- Rastel D, Abdouh A, Dahl D, et al. An original organotypic culture method to study the organ of Corti of the newborn rat in vitro. J Neurosci Methods. 1993;47:123–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

