Investigating the utility of previously developed prediction scores in acute ischemic stroke patients in the stroke belt
- PMID: 25113079
- PMCID: PMC4780244
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2014.02.003
Investigating the utility of previously developed prediction scores in acute ischemic stroke patients in the stroke belt
Abstract
Background: To assess the utility of previously developed scoring systems, we compared SEDAN, named after the components of the score (baseline blood Sugar, Early infarct signs and (hyper) Dense cerebral artery sign on admission computed tomography scan, Age, and National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale on admission), Totaled Health Risks in Vascular Events (THRIVE), Houston Intra-arterial Therapy (HIAT), and HIAT-2 scoring systems among patients receiving systemic (intravenous [IV] tissue plasminogen activator [tPA]) and endovascular (intra-arterial [IA]) treatments.
Methods: We retrospectively reviewed all IV tPA and IA patients presenting to our center from 2008-2011. The scores were assessed in patients who were treated with IV tPA only, IA only, and a combination of IV tPA and IA (IV-IA). We tested the ability of THRIVE to predict discharge modified Rankin scale (mRS) 3-6, HIAT and HIAT-2 discharge mRS 4-6, and SEDAN symptomatic intracerebral hemorrhage (sICH).
Results: Of the 366 patients who were included in this study, 243 had IV tPA only, 89 had IA only, and 34 had IV-IA. THRIVE was predictive of mRS 3-6 in the IV-IA (odds ratio [OR], 1.95; 95% confidence interval [CI], 1.30-2.91) and the IV group (OR, 1.71; 95% CI, 1.43-2.04), but not in the IA group. HIAT was predictive of mRS 4-6 in the IA (OR, 3.55; 95% CI, 1.65-7.25), IV (OR, 3.47; 95% CI, 2.26-5.33), and IV-IA group (OR, 6.48; 95% CI, 1.41-29.71). HIAT-2 was predictive of mRS 4-6 in the IA (OR, 1.39; 95% CI, 1.03-1.87) and IV group (OR, 1.36; 95% CI, 1.18-1.57), but not in the IV-IA group. SEDAN was not predictive of sICH in the IA or the IV-IA group, but was predictive in the IV group (OR, 1.54; 95% CI, 1.01-2.36).
Conclusions: Our study demonstrated that although highly predictive of outcome in the original study design treatment groups, prediction scores may not generalize to all patient samples, highlighting the importance of validating prediction scores in diverse samples.
Keywords: Stroke; epidemiology; outcome; stroke recovery.
Copyright © 2014 National Stroke Association. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
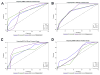
References
-
- Towfighi A, Saver JL. Stroke declines from third to fourth leading cause of death in the United States: historical perspective and challenges ahead. Stroke. 2011;42:2351–2355. - PubMed
-
- Tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Stroke Study Group. N Engl J Med. 1995;333:1581–1587. - PubMed
-
- Hacke W, Kaste M, Bluhmki E, et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase 3 to 4. 5 hours after acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:1317–1329. - PubMed
-
- Reeves MJ, Arora S, Broderick JP, et al. Acute stroke care in the US: results from 4 pilot prototypes of the Paul Coverdell National Acute Stroke Registry. Stroke. 2005;36:1232–1240. - PubMed
-
- Grotta JC, Burgin WS, El-Mitwalli A, et al. Intravenous tissue-type plasminogen activator therapy for ischemic stroke: Houston experience 1996 to 2000. Arch Neurol. 2001;58:2009–2013. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

