Dissecting the complement pathway in hepatic injury and regeneration with a novel protective strategy
- PMID: 25113972
- PMCID: PMC4144741
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20131902
Dissecting the complement pathway in hepatic injury and regeneration with a novel protective strategy
Abstract
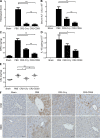
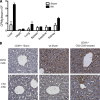
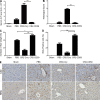
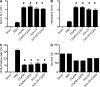
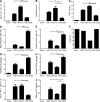
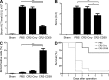
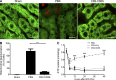
Liver resection is commonly performed under ischemic conditions, resulting in two types of insult to the remnant liver: ischemia reperfusion injury (IRI) and loss of liver mass. Complement inhibition is recognized as a potential therapeutic modality for IRI, but early complement activation products are also essential for liver regeneration. We describe a novel site-targeted murine complement inhibitor, CR2-CD59, which specifically inhibits the terminal membrane attack complex (MAC), and we use this protein to investigate the complement-dependent balance between liver injury and regeneration in a clinical setting of pharmacological inhibition. CR2-CD59 did not impact in vivo generation of C3 and C5 activation products but was as effective as the C3 activation inhibitor CR2-Crry at ameliorating hepatic IRI, indicating that the MAC is the principle mediator of hepatic IRI. Furthermore, unlike C3 or C5 inhibition, CR2-CD59 was not only protective but significantly enhanced hepatocyte proliferation after partial hepatectomy, including when combined with ischemia and reperfusion. Remarkably, CR2-CD59 also enhanced regeneration after 90% hepatectomy and improved long-term survival from 0 to 70%. CR2-CD59 functioned by increasing hepatic TNF and IL-6 levels with associated STAT3 and Akt activation, and by preventing mitochondrial depolarization and allowing recovery of ATP stores.
© 2014 Marshall et al.
Figures


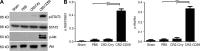
References
-
- Amsterdam, E.A., Stahl G.L., Pan H.L., Rendig S.V., Fletcher M.P., and Longhurst J.C.. 1995. Limitation of reperfusion injury by a monoclonal antibody to C5a during myocardial infarction in pigs. Am. J. Physiol. 268:H448–H457. - PubMed
-
- Arumugam, T.V., Woodruff T.M., Stocks S.Z., Proctor L.M., Pollitt S., Shiels I.A., Reid R.C., Fairlie D.P., and Taylor S.M.. 2004. Protective effect of a human C5a receptor antagonist against hepatic ischaemia-reperfusion injury in rats. J. Hepatol. 40:934–941. 10.1016/j.jhep.2004.02.017 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Atkinson, C., Song H., Lu B., Qiao F., Burns T.A., Holers V.M., Tsokos G.C., and Tomlinson S.. 2005. Targeted complement inhibition by C3d recognition ameliorates tissue injury without apparent increase in susceptibility to infection. J. Clin. Invest. 115:2444–2453. 10.1172/JCI25208 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

