Inhibitor of MYC identified in a Kröhnke pyridine library
- PMID: 25114221
- PMCID: PMC4151726
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1319488111
Inhibitor of MYC identified in a Kröhnke pyridine library
Abstract
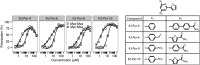
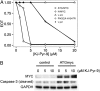
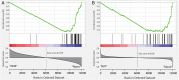
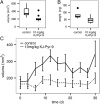
In a fluorescence polarization screen for the MYC-MAX interaction, we have identified a novel small-molecule inhibitor of MYC, KJ-Pyr-9, from a Kröhnke pyridine library. The Kd of KJ-Pyr-9 for MYC in vitro is 6.5 ± 1.0 nM, as determined by backscattering interferometry; KJ-Pyr-9 also interferes with MYC-MAX complex formation in the cell, as shown in a protein fragment complementation assay. KJ-Pyr-9 specifically inhibits MYC-induced oncogenic transformation in cell culture; it has no or only weak effects on the oncogenic activity of several unrelated oncoproteins. KJ-Pyr-9 preferentially interferes with the proliferation of MYC-overexpressing human and avian cells and specifically reduces the MYC-driven transcriptional signature. In vivo, KJ-Pyr-9 effectively blocks the growth of a xenotransplant of MYC-amplified human cancer cells.
Keywords: combinatorial library; gene signature; protein–protein interactions; transcriptional control; xenograft.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Lee LA, Dang CV. Myc target transcriptomes. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2006;302:145–167. - PubMed
-
- Eisenman RN. The Max network: Coordinated transcriptional regulation of cell growth and proliferation. Harvey Lect. 2000–2001;96:1–32. - PubMed
-
- Eisenman RN. Deconstructing Myc. Genes Dev. 2001;15(16):2023–2030. - PubMed
-
- Blackwood EM, Eisenman RN. Max: A helix-loop-helix zipper protein that forms a sequence-specific DNA-binding complex with Myc. Science. 1991;251(4998):1211–1217. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

