Quasi-resonant circulation regimes and hemispheric synchronization of extreme weather in boreal summer
- PMID: 25114245
- PMCID: PMC4151761
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1412797111
Quasi-resonant circulation regimes and hemispheric synchronization of extreme weather in boreal summer
Abstract
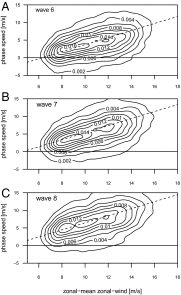
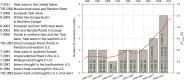
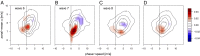
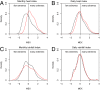
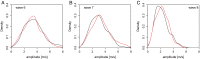
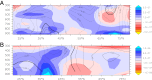
The recent decade has seen an exceptional number of high-impact summer extremes in the Northern Hemisphere midlatitudes. Many of these events were associated with anomalous jet stream circulation patterns characterized by persistent high-amplitude quasi-stationary Rossby waves. Two mechanisms have recently been proposed that could provoke such patterns: (i) a weakening of the zonal mean jets and (ii) an amplification of quasi-stationary waves by resonance between free and forced waves in midlatitude waveguides. Based upon spectral analysis of the midtroposphere wind field, we show that the persistent jet stream patterns were, in the first place, due to an amplification of quasi-stationary waves with zonal wave numbers 6-8. However, we also detect a weakening of the zonal mean jet during these events; thus both mechanisms appear to be important. Furthermore, we demonstrate that the anomalous circulation regimes lead to persistent surface weather conditions and therefore to midlatitude synchronization of extreme heat and rainfall events on monthly timescales. The recent cluster of resonance events has resulted in a statistically significant increase in the frequency of high-amplitude quasi-stationary waves of wave numbers 7 and 8 in July and August. We show that this is a robust finding that holds for different pressure levels and reanalysis products. We argue that recent rapid warming in the Arctic and associated changes in the zonal mean zonal wind have created favorable conditions for double jet formation in the extratropics, which promotes the development of resonant flow regimes.
Keywords: Arctic amplification; climate change; climate impact; midlatitude weather; planetary waves.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Westra S, Alexander LV, Zwiers FW. Global increasing trends in annual maximum daily precipitation. J Clim. 2013;26(11):3904–3918.
-
- Zhang X, Wan H, Zwiers FW, Hegerl GC, Min S-K. Attributing intensification of precipitation extremes to human influence. Geophys Res Lett. 2013;40(19):5252–5257.
-
- Sillmann J, Kharin VV, Zhang X, Zwiers FW, Bronaugh D. Climate extremes indices in the CMIP5 multi-model ensemble. Part 1 : Model evaluation in the present. J Geophys Res. 2013;118(4):1716–1733.
-
- Coumou D, Robinson A, Rahmstorf S. Global increase in record-breaking monthly-mean temperatures. Clim Change. 2013;118(3-4):771–782.
-
- Coumou D, Robinson A. Historic and future increase in the global land area affected by monthly heat extremes. Environ Res Lett. 2013;8(3):034018.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

