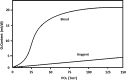
Blood substitutes: possibilities with nanotechnology
- PMID: 25114400
- PMCID: PMC4115085
- DOI: 10.1007/s12288-013-0309-5
Blood substitutes: possibilities with nanotechnology
Abstract
Nanotechnology deals with molecules in the nanometer (10(-9)) range and is currently being used successfully in the field of medicine. Nanotechnology has important implications in nearly all the branches of medicine and it has all the capabilities to revolutionize the vast field of medicine in future. Nanotechnological advancements have been used for the preparation of artificial hemoglobin. It is formed by assembling the hemoglobin molecules into a soluble complex. A recent approach includes the assembling of this artificial hemoglobin with enzymes such as catalase and superoxide dismutase into a nano-complex. This complex acts as an oxygen carrier as well as an antioxidant in conditions with ischemia-reperfusion injuries.
Keywords: Artificial red cells; Blood substitutes; Nanotechnology; Polyhemoglobin.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Nanobiotechnology for hemoglobin-based blood substitutes.Crit Care Clin. 2009 Apr;25(2):373-82, Table of Contents. doi: 10.1016/j.ccc.2008.12.006. Crit Care Clin. 2009. PMID: 19341914 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nanobiotechnological modification of hemoglobin and enzymes from this laboratory.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008 Oct;1784(10):1435-40. doi: 10.1016/j.bbapap.2008.05.006. Epub 2008 Jun 17. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2008. PMID: 18565337 Free PMC article.
-
Extraction of erythrocyte enzymes for the preparation of polyhemoglobin-catalase-superoxide dismutase.Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol. 2009;37(2):69-77. doi: 10.1080/10731190902742240. Epub 2009 Feb 18. Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol. 2009. PMID: 19229698 Free PMC article.
-
Blood replacement with nanobiotechnologically engineered hemoglobin and hemoglobin nanocapsules.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2010 Jul-Aug;2(4):418-30. doi: 10.1002/wnan.95. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2010. PMID: 20564467 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Evolution of artificial cells using nanobiotechnology of hemoglobin based RBC blood substitute as an example.Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol. 2006;34(6):551-66. doi: 10.1080/10731190600973808. Artif Cells Blood Substit Immobil Biotechnol. 2006. PMID: 17090428 Review.
Cited by
-
Nanomedicines: A Potential Treatment for Blood Disorder Diseases.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019 Nov 28;7:369. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2019.00369. eCollection 2019. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2019. PMID: 31850329 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thalassemia in Sub-Saharan Africa: epidemiology, diagnosis, and management - a narrative review.Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025 Apr 10;87(6):3523-3536. doi: 10.1097/MS9.0000000000003270. eCollection 2025 Jun. Ann Med Surg (Lond). 2025. PMID: 40486599 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Thalassemia and Nanotheragnostics: Advanced Approaches for Diagnosis and Treatment.Biosensors (Basel). 2023 Apr 1;13(4):450. doi: 10.3390/bios13040450. Biosensors (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37185525 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aggarwal S, Sharma V. Attitudes and problems related to voluntary blood donation in India: a short communication. Ann Trop Med Public Health. 2012;5:50–52.
-
- Blood safety and clinical technology. Available at-http://www.searo.who.int/en/section10/section17/section1976.htm
-
- Chaitanya kumar IS, Yashoverdhan Efforts to meet the challenges of 100 % voluntary blood donation. Asian J Transfus Sci. 2011;5:68–69. doi: 10.4103/0973-6247.76006. - DOI
-
- Based on WHO Global Database on Blood Safety (GDBS) 2008, with responses received from 164 countries, covering 92 % of the world’s population. Available at http://www.who.int/bloodsafety/global_database/GDBS_Summary_Report_2011.pdf
-
- Geyer RP, Monroe RG, Taylor K. Survival of rats having red cells totally replaced with emulsified fluorocarbon. Federation Proc. 1968;27:384–390.
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources