Design, implementation, and evaluation of a pediatric and adolescent type 2 diabetes management program at a tertiary pediatric center
- PMID: 25114539
- PMCID: PMC4124128
- DOI: 10.2147/JMDH.S63842
Design, implementation, and evaluation of a pediatric and adolescent type 2 diabetes management program at a tertiary pediatric center
Abstract
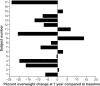
Global rates of type 2 diabetes in children and adolescents have increased significantly over the past three decades. Type 2 diabetes is a relatively new disease in this age group, and there is a dearth of information about how to structure treatment programs to manage its comorbidities and complications. In this paper, we describe the design and implementation of a personalized multidisciplinary, family-centered, pediatric and adolescent type 2 diabetes program at a tertiary pediatric center in Hamilton, Ontario, Canada. We report the process of designing and implementing such a program, and show that this multidisciplinary program led to improvement in glycated hemoglobin (n=17, 8% at baseline versus 6.4% at 1 year, 95% confidence interval (0.1-0.28), P-value <0.0001) and stabilized body mass index, with lowered C-peptide and no change in fitness or metabolic biomarkers of lipid metabolism and liver function. As type 2 diabetes becomes more prevalent in youth, the need for programs that successfully address the complex nature of this disease is central to its management and to mitigate its long-term adverse outcomes.
Keywords: adolescents; multidisciplinary; pediatric; program design; type 2 diabetes.
Figures
References
-
- Whiting DR, Guariguala L, Weil C, Shaw J. IDF diabetes atlas: global estimates of the prevalence of diabetes for 2011 and 2030. Diabetes Res Clin Pract. 2011;94(3):311–321. - PubMed
-
- Pinhas-Hamiel O, Zeitler P. The global spread of type 2 diabetes mellitus in children and adolescents. J Pediatr. 2005;146(5):693–700. - PubMed
-
- Rosenbloom AL, Joe JR, Young RS, Winter WE. Emerging epidemic of type 2 diabetes in youth. Diabetes Care. 1999;22(2):345–354. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

