A review of hydrofluoric acid burn management
- PMID: 25114621
- PMCID: PMC4116323
A review of hydrofluoric acid burn management
Abstract
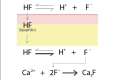
Hydrofluoric acid (HF) causes a unique chemical burn. Much of the current treatment knowledge of HF burns is derived from case reports, small case series, animal studies and anecdotal evidence. The management can be challenging because clinical presentation and severity of these burns vary widely. Plastic surgeons managing burn patients must have a basic understanding of the pathophysiology, the range of severity in presentation and the current treatment options available for HF burns. The present article reviews the current understanding of the pathophysiology and systemic effects associated with severe HF burns. Furthermore, it distinguishes between minor and life-threatening HF burns and describes several of the basic techniques that are available to treat patients with HF burns.
L’acide fluorhydrique (AF) provoque une brûlure chimique bien particulière. La plus grande partie des connaissances actuelles sur les brûlures à l’AF sont dérivées de rapports de cas, de petites séries de cas, d’études sur des animaux et d’observations isolées. La prise en charge peut être difficile, car la présentation clinique et la gravité des brûlures sont très variées. Les plasticiens qui traitent les patients brûlés doivent posséder des connaissances de base sur la physiopathologie, les divers degrés de gravité de présentation et les possibilités thérapeutiques offertes pour soigner les brûlures à l’AF.Le présent article contient une analyse des connaissances sur la physiopathologie et les effets systémiques des graves brûlures à l’AF. Il fait également la distinction entre les brûlures à l’AF mineures et celles au potentiel fatal et contient une description de quelques-unes des techniques de base offertes pour traiter les patients ayant des brûlures à l’AF.
Keywords: Acid; Hydrofluoric; Review.
Figures
References
-
- Caravati M. Acute hydrofluoric acid exposure. Am J Emerg Med. 1988;6:143–50. - PubMed
-
- Kirkpatrick J, Burd D. Hydrofluoric acid burns: A review. Burns. 1995;21:483–93. - PubMed
-
- Upfal M, Doyle C. Medical management of hydrofluoric acid exposure. J Occup Med. 1990:726–31. - PubMed
-
- Stuke LE, Arnoldo BD, Hunt JL, Purdue GF. Hydrofluoric acid burns: A 15-year experience. J Burn Care Res. 2008;29:893–6. - PubMed
-
- Hatzifotis M, Williams A, Muller M, Pegg S. Hydrofluoric acid burns. Burns. 2004;30:156–9. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
