Antidiabetic effect of Sida cordata in alloxan induced diabetic rats
- PMID: 25114914
- PMCID: PMC4119905
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/671294
Antidiabetic effect of Sida cordata in alloxan induced diabetic rats
Abstract
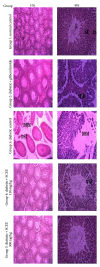
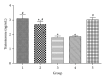
Medicinal plants are efficient ameliorator of oxidative stress associated with diabetes mellitus. In this study, ethyl acetate fraction (SCEE) of Sida cordata was investigated for scientific validation of its folk use in diabetes. Antidiabetic effect of SCEE was confirmed by antihyperglycemic activity in normal glucose loaded and diabetic glucose loaded animals as well as normal off feed animals. Confirmation of antidiabetic activity and toxicity ameliorative role of S. cordata was investigated in a chronic multiple dose treatment study of fifteen days. A single dose of alloxan (120 mg/kg) produced a decrease in insulin level, hyperglycemia, elevated total lipids, triglycerides, and cholesterol and decreased the high-density lipoproteins. Concurrent with these changes, there was an increase in the concentration of lipid peroxidation (TBARS), H2O2, and nitrite in pancreas, liver, and testis. This oxidative stress was related to a decrease in glutathione content (GSH) and antioxidant enzymes. Administration of SCEE for 15 days after diabetes induction ameliorated hyperglycemia, restored lipid profile, blunted the increase in TBARS, H2O2, and nitrite content, and stimulated the GSH production in the organs of alloxan-treated rats. We suggested that SCEE could be used as antidiabetic component in case of diabetes mellitus. This may be related to its antioxidative properties.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Antidiabetic and antioxidant potential of Alnus nitida leaves in alloxan induced diabetic rats.J Ethnopharmacol. 2020 Apr 6;251:112544. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2020.112544. Epub 2020 Jan 3. J Ethnopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31904496
-
Phytochemical investigation and nephroprotective potential of Sida cordata in rat.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017 Aug 4;17(1):388. doi: 10.1186/s12906-017-1896-8. BMC Complement Altern Med. 2017. PMID: 28778164 Free PMC article.
-
Antihyperglycemic and antioxidant effect of hydroethanolic extract of Butea monosperma bark in diabetic mice.Indian J Biochem Biophys. 2012 Feb;49(1):55-62. Indian J Biochem Biophys. 2012. PMID: 22435145
-
Acute and chronic hypoglycemic activity of Sida tiagii fruits in N5-streptozotocin diabetic rats.Acta Pol Pharm. 2012 Jul-Aug;69(4):699-706. Acta Pol Pharm. 2012. PMID: 22876613
-
Antidiabetic Potential of Plants from the Caribbean Basin.Plants (Basel). 2022 May 20;11(10):1360. doi: 10.3390/plants11101360. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35631785 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-Diabetic Effects of Allium hookeri Extracts Prepared by Different Methods in Type 2 C57BL/J-db/db Mice.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022 Apr 17;15(4):486. doi: 10.3390/ph15040486. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35455483 Free PMC article.
-
Amelioration of antioxidant potential, toxicity, and antihyperglycemic activity of Hippophae salicifolia D. Don leaf extracts in alloxan-induced diabetic rats.3 Biotech. 2019 Aug;9(8):308. doi: 10.1007/s13205-019-1840-3. Epub 2019 Jul 27. 3 Biotech. 2019. PMID: 31355117 Free PMC article.
-
Antidiabetic Activity of Picris japonica Thunb Aqueous Extract in Diabetic KK-Ay Mice.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018 Nov 12;2018:1298030. doi: 10.1155/2018/1298030. eCollection 2018. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2018. PMID: 30538754 Free PMC article.
-
Hyperglycemia-associated Alzheimer's-like symptoms and other behavioral effects attenuated by Plumeria obtusa L. Extract in alloxan-induced diabetic rats.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Dec 16;13:1077570. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.1077570. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 36588726 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of olive leaves extract on the antidiabetic effect of glyburide for possible herb-drug interaction.Saudi Pharm J. 2019 Dec;27(8):1182-1195. doi: 10.1016/j.jsps.2019.10.001. Epub 2019 Oct 11. Saudi Pharm J. 2019. PMID: 31885478 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Paik S-G, Blue ML, Fleischer N, Shin S-I. Diabetes susceptibility of BALB/cBOM mice treated with streptozotocin: inhibition by lethal irradiation and restoration by splenic lymphocytes. Diabetes. 1982;31(9):808–815. - PubMed
-
- Kataoka S, Satoh J, Fujiya H, et al. Immunologic aspects of the nonobese diabetic (NOD) mouse: abnormalities of cellular immunity. Diabetes. 1983;32(3):247–253. - PubMed
-
- Kesavulu MM, Girl R, Kameswara Rao B, Apparao CH. Lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme levels in type 2 diabetics with microvascular complications. Diabetes and Metabolism. 2000;26(5):387–392. - PubMed
-
- Scoppola A, Montecchi FR, Menzinger G, Lala A. Urinary mevalonate excretion rate in type 2 diabetes: role of metabolic control. Atherosclerosis. 2001;156(2):357–361. - PubMed
-
- Ugochukwu NH, Babady NE, Cobourne M, Gasset SR. The effect of Gongronema latifolium extracts on serum lipid profile and oxidative stress in hepatocytes of diabetic rats. Journal of Biosciences. 2003;28(1):1–5. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

