Geodermatophilus poikilotrophi sp. nov.: a multitolerant actinomycete isolated from dolomitic marble
- PMID: 25114928
- PMCID: PMC4119925
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/914767
Geodermatophilus poikilotrophi sp. nov.: a multitolerant actinomycete isolated from dolomitic marble
Abstract
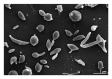
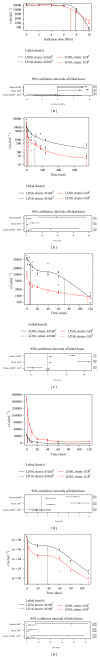
A novel Gram-reaction-positive, aerobic actinobacterium, tolerant to mitomycin C, heavy metals, metalloids, hydrogen peroxide, desiccation, and ionizing- and UV-radiation, designated G18T, was isolated from dolomitic marble collected from outcrops in Samara (Namibia). The growth range was 15-35°C, at pH 5.5-9.5 and in presence of 1% NaCl, forming greenish-black coloured colonies on GYM Streptomyces agar. Chemotaxonomic and molecular characteristics of the isolate matched those described for other representatives of the genus Geodermatophilus. The peptidoglycan contained meso-diaminopimelic acid as diagnostic diaminoacid. The main phospholipids were phosphatidylethanolamine, phosphatidylcholine, phosphatidylinositol, and small amount of diphosphatidylglycerol. MK-9(H4) was the dominant menaquinone and galactose was detected as diagnostic sugar. The major cellular fatty acids were branched-chain saturated acids iso-C16:0 and iso-C15:0 and the unsaturated C17:1 ω8c and C16:1 ω7c. The 16S rRNA gene showed 97.4-99.1% sequence identity with the other representatives of genus Geodermatophilus. Based on phenotypic results and 16S rRNA gene sequence analysis, strain G18T is proposed to represent a novel species, Geodermatophilus poikilotrophi. Type strain is G18T (=DSM 44209T=CCUG 63018T). The INSDC accession number is HF970583. The novel R software package lethal was used to compute the lethal doses with confidence intervals resulting from tolerance experiments.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Description of gamma radiation-resistant Geodermatophilus dictyosporus sp. nov. to accommodate the not validly named Geodermatophilus obscurus subsp. dictyosporus (Luedemann, 1968).Extremophiles. 2015 Jan;19(1):77-85. doi: 10.1007/s00792-014-0708-z. Epub 2014 Nov 16. Extremophiles. 2015. PMID: 25399311
-
Geodermatophilus telluris sp. nov., an actinomycete isolated from Saharan desert sand.Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2013 Jun;63(Pt 6):2254-2259. doi: 10.1099/ijs.0.046888-0. Epub 2012 Nov 16. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 2013. PMID: 23159748
-
Description of Geodermatophilus amargosae sp. nov., to accommodate the not validly named Geodermatophilus obscurus subsp. amargosae (Luedemann, 1968).Curr Microbiol. 2014 Mar;68(3):365-71. doi: 10.1007/s00284-013-0479-2. Epub 2013 Nov 8. Curr Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24202736
-
Geodermatophilus africanus sp. nov., a halotolerant actinomycete isolated from Saharan desert sand.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2013 Aug;104(2):207-16. doi: 10.1007/s10482-013-9939-8. Epub 2013 May 31. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2013. PMID: 23723018
-
Geodermatophilus siccatus sp. nov., isolated from arid sand of the Saharan desert in Chad.Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2013 Mar;103(3):449-56. doi: 10.1007/s10482-012-9824-x. Epub 2012 Oct 18. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 2013. PMID: 23076796
Cited by
-
Spatially explicit depiction of a floral epiphytic bacterial community reveals role for environmental filtering within petals.Microbiologyopen. 2021 Jan;10(1):e1158. doi: 10.1002/mbo3.1158. Microbiologyopen. 2021. PMID: 33650801 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Scale Data Call for a Taxonomic Rearrangement of Geodermatophilaceae.Front Microbiol. 2017 Dec 19;8:2501. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02501. eCollection 2017. Front Microbiol. 2017. PMID: 29312207 Free PMC article.
-
Characterization of black patina from the Tiber River embankments using Next-Generation Sequencing.PLoS One. 2020 Jan 9;15(1):e0227639. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227639. eCollection 2020. PLoS One. 2020. PMID: 31917800 Free PMC article.
-
Description of gamma radiation-resistant Geodermatophilus dictyosporus sp. nov. to accommodate the not validly named Geodermatophilus obscurus subsp. dictyosporus (Luedemann, 1968).Extremophiles. 2015 Jan;19(1):77-85. doi: 10.1007/s00792-014-0708-z. Epub 2014 Nov 16. Extremophiles. 2015. PMID: 25399311
-
Lack of correlation of desiccation and radiation tolerance in microorganisms from diverse extreme environments tested under anoxic conditions.FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2018 Mar 1;365(6):fny044. doi: 10.1093/femsle/fny044. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 2018. PMID: 29474542 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Normand P, Orso S, Cournoyer B, et al. Molecular phylogeny of the genus Frankia and related genera and emendation of the family Frankiaceae. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology. 1996;46(1):1–9. - PubMed
-
- Normand P. Geodermatophilaceae fam. nov., a formal description. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 2006;56, part 10:2277–2278. - PubMed
-
- Skerman VBD, McGowan V, Sneath PHA. Approved lists of bacterial names. International Journal of Systematic Bacteriology. 1980;30(1):225–420.
-
- Montero-Calasanz MD, Göker M, Pötter G, et al. Geodermatophilus africanus sp. nov., a halotolerant actinomycete isolated from Saharan desert sand. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek. 2013;104(2):207–216. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

