Andrographolide inhibits nuclear factor-κB activation through JNK-Akt-p65 signaling cascade in tumor necrosis factor-α-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells
- PMID: 25114952
- PMCID: PMC4121194
- DOI: 10.1155/2014/130381
Andrographolide inhibits nuclear factor-κB activation through JNK-Akt-p65 signaling cascade in tumor necrosis factor-α-stimulated vascular smooth muscle cells
Abstract
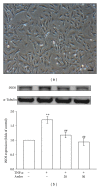
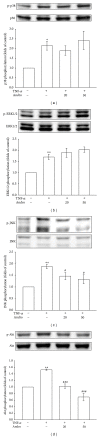
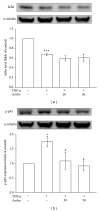
Critical vascular inflammation leads to vascular dysfunction and cardiovascular diseases, including abdominal aortic aneurysms, hypertension, and atherosclerosis. Andrographolide is the most active and critical constituent isolated from the leaves of Andrographis paniculata, a herbal medicine widely used for treating anti-inflammation in Asia. In this study, we investigated the mechanisms of the inhibitory effects of andrographolide in vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs) exposed to a proinflammatory stimulus, tumor necrosis factor-α (TNF-α). Treating TNF-α-stimulated VSMCs with andrographolide suppressed the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase in a concentration-dependent manner. A reduction in TNF-α-induced c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), Akt, and p65 phosphorylation was observed in andrographolide-treated VSMCs. However, andrographolide affected neither IκBα degradation nor p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase or extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 phosphorylation under these conditions. Both treatment with LY294002, a phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt inhibitor, and treatment with SP600125, a JNK inhibitor, markedly reversed the andrographolide-mediated inhibition of p65 phosphorylation. In addition, LY294002 and SP600125 both diminished Akt phosphorylation, whereas LY294002 had no effects on JNK phosphorylation. These results collectively suggest that therapeutic interventions using andrographolide can benefit the treatment of vascular inflammatory diseases, and andrographolide-mediated inhibition of NF-κB activity in TNF-α-stimulated VSMCs occurs through the JNK-Akt-p65 signaling cascade, an IκBα-independent mechanism.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Andrographolide enhances nuclear factor-kappaB subunit p65 Ser536 dephosphorylation through activation of protein phosphatase 2A in vascular smooth muscle cells.J Biol Chem. 2011 Feb 25;286(8):5942-55. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.123968. Epub 2010 Dec 17. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21169355 Free PMC article.
-
PMC, a potent hydrophilic α-tocopherol derivative, inhibits NF-κB activation via PP2A but not IκBα-dependent signals in vascular smooth muscle cells.J Cell Mol Med. 2014 Jul;18(7):1278-89. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.12277. Epub 2014 Apr 13. J Cell Mol Med. 2014. PMID: 24725826 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of NF-κB signaling by andrographolide with a novel mechanism in human platelets: regulatory roles of the p38 MAPK-hydroxyl radical-ERK2 cascade.Biochem Pharmacol. 2012 Oct 1;84(7):914-24. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2012.06.030. Epub 2012 Jul 4. Biochem Pharmacol. 2012. PMID: 22771630
-
A review on the molecular basis underlying the protective effects of Andrographis paniculata and andrographolide against myocardial injury.Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021 Nov 10;15:4615-4632. doi: 10.2147/DDDT.S331027. eCollection 2021. Drug Des Devel Ther. 2021. PMID: 34785890 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting signaling pathways with andrographolide in cancer therapy (Review).Mol Clin Oncol. 2024 Sep 5;21(5):81. doi: 10.3892/mco.2024.2779. eCollection 2024 Nov. Mol Clin Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39301125 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Novel wine in an old bottle: Preventive and therapeutic potentials of andrographolide in atherosclerotic cardiovascular diseases.J Pharm Anal. 2023 Jun;13(6):563-589. doi: 10.1016/j.jpha.2023.05.010. Epub 2023 May 20. J Pharm Anal. 2023. PMID: 37440909 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Andrographolide, a New Hope in the Prevention and Treatment of Metabolic Syndrome.Front Pharmacol. 2017 Aug 23;8:571. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2017.00571. eCollection 2017. Front Pharmacol. 2017. PMID: 28878680 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical study of different doses of atorvastatin combined with febuxostat in patients with gout and carotid atherosclerosis.Pak J Med Sci. 2020 Sep-Oct;36(6):1334-1338. doi: 10.12669/pjms.36.6.2945. Pak J Med Sci. 2020. PMID: 32968404 Free PMC article.
-
Andrographolide as a Therapeutic Agent Against Breast and Ovarian Cancers.Open Life Sci. 2019 Dec 4;14:462-469. doi: 10.1515/biol-2019-0052. eCollection 2019 Jan. Open Life Sci. 2019. PMID: 33817182 Free PMC article.
-
Activity of andrographolide against chikungunya virus infection.Sci Rep. 2015 Sep 18;5:14179. doi: 10.1038/srep14179. Sci Rep. 2015. PMID: 26384169 Free PMC article.
References
-
- McKellar GE, McCarey DW, Sattar N, McInnes IB. Role for TNF in atherosclerosis? Lessons from autoimmune disease. Nature reviews. Cardiology. 2009;6(6):410–417. - PubMed
-
- Cartwright N, Murch O, McMaster SK, et al. Selective NOD1 agonists cause shock and organ injury/dysfunction in vivo. The American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine. 2007;175(6):595–603. - PubMed
-
- Hattori Y, Matsumura M, Kasai K. Vascular smooth muscle cell activation by C-reactive protein. Cardiovascular Research. 2003;58(1):186–195. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

